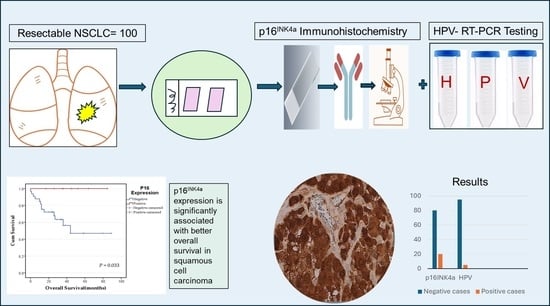
Background and Objectives: Human papillomavirus (HPV) was previously investigated in lung cancer with wide inter-geographic discrepancies. p16
INK4a has been used as a surrogate for detecting high-risk HPV (HR-HPV) in some cancer types. This study assessed the evidence of HPV in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) among Jordanian patients, investigated the expression of p16
INK4a, and evaluated its prognostic value and association with HPV status.
Materials and Methods: The archived samples of 100 patients were used. HPV DNA detection was performed by real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). p16
INK4a expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry (IHC). The Eighth American Joint Committee on Cancer protocol (AJCC) of head and neck cancer criteria were applied to evaluate p16
INK4a positivity considering a moderate/strong nuclear/cytoplasmic expression intensity with a distribution in ≥75% of cells as positive.
Results: HPV DNA was detected in 5% of NSCLC cases. Three positive cases showed HR-HPV subtypes (16, 18, 52), and two cases showed the probable HR-HPV 26 subtype. p16
INK4a expression was positive in 20 (20%) NSCLC cases. None of the HPV-positive tumors were positive for p16
INK4a expression. A statistically significant association was identified between p16
INK4a expression and the pathological stage (
p = 0.029) but not with other variables. No survival impact of p16
INK4a expression was detected in NSCLC cases as a group; however, it showed a statistically significant association with overall survival (OS) in squamous cell carcinoma (SqCC) cases (
p = 0.033).
Conclusions: This is the first study to assess HPV and p16
INK4a expression in a Jordanian population. HPV positivity is rare in NSCLC among a Jordanian subpopulation. P16
INK4a reliability as a surrogate marker for HPV infection in lung cancer must be revisited.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT