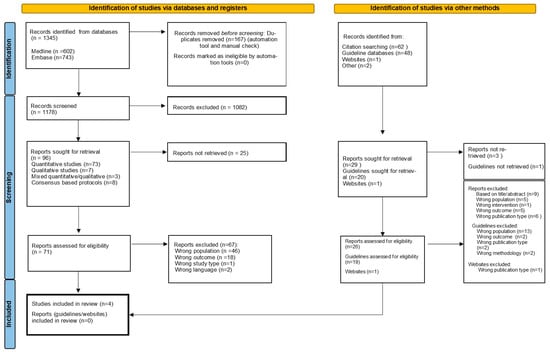
In recent years, the incidence of fungal infections in humans has increased dramatically, accompanied by an expansion in the number of species implicated as etiological agents, especially environmental fungi never involved before in human infection. Among fungal pathogens,
Candida species are the most
[...] Read more.
In recent years, the incidence of fungal infections in humans has increased dramatically, accompanied by an expansion in the number of species implicated as etiological agents, especially environmental fungi never involved before in human infection. Among fungal pathogens,
Candida species are the most common opportunistic fungi that can cause local and systemic infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
Candida albicans (
C. albicans) is the most common causative agent of mucosal and healthcare-associated systemic infections. However, during recent decades, there has been a worrying increase in the number of emerging multi-drug-resistant non-
albicans Candida (NAC) species, i.e.,
C. glabrata,
C. parapsilosis,
C. tropicalis,
C. krusei,
C. auris, and
C. ciferrii. In particular,
Candida ciferrii, also known as
Stephanoascus ciferrii or
Trichomonascus ciferrii, is a heterothallic ascomycete yeast-like fungus that has received attention in recent decades as a cause of local and systemic fungal diseases. Today, the new definition of the
S. ciferrii complex, which consists of
S. ciferrii,
Candida allociferrii, and
Candida mucifera, was proposed after sequencing the 18S rRNA gene. Currently, the
S. ciferrii complex is mostly associated with non-severe ear and eye infections, although a few cases of severe candidemia have been reported in immunocompromised individuals. Low susceptibility to currently available antifungal drugs is a rising concern, especially in NAC species. In this regard, a high rate of resistance to azoles and more recently also to echinocandins has emerged in the
S. ciferrii complex. This review focuses on epidemiological, biological, and clinical aspects of the
S. ciferrii complex, including its pathogenicity and drug resistance.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT