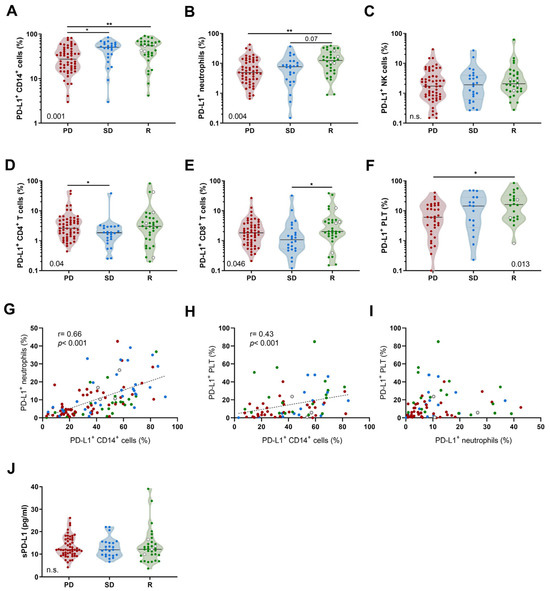
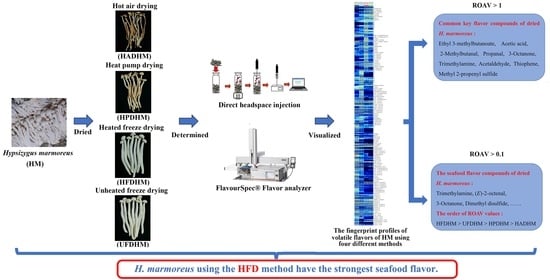
Gas chromatography–ion mobility spectroscopy (GC-IMS) was used to analyze the volatile components in dried
Hypsizygus marmoreus of different drying methods, including hot air drying (HAD), heat pump drying (HPD), heated freeze-drying (HFD), and unheated freeze-drying (UFD). A total of 116 signal peaks corresponding
[...] Read more.
Gas chromatography–ion mobility spectroscopy (GC-IMS) was used to analyze the volatile components in dried
Hypsizygus marmoreus of different drying methods, including hot air drying (HAD), heat pump drying (HPD), heated freeze-drying (HFD), and unheated freeze-drying (UFD). A total of 116 signal peaks corresponding to 96 volatile compounds were identified, including 25 esters, 24 aldehydes, 23 alcohols, 13 ketones, 10 heterocyclic compounds, 8 carboxylic acids, 7 terpenes, 3 sulfur-containing compounds, 2 nitrogen-containing compounds, and 1 aromatic hydrocarbon. The total content of volatile compounds in
H. marmoreus dried by the four methods, from highest to lowest, was as follows: HAD, HPD, HFD, and UFD. The main volatile compounds included carboxylic acids, alcohols, esters, and aldehydes. Comparing the peak intensities of volatile compounds in dried
H. marmoreus using different drying methods, it was found that the synthesis of esters, aldehydes, and terpenes increased under hot drying methods such as HAD and HPD, while the synthesis of compounds containing sulfur and nitrogen increased under freeze-drying methods such as HFD and UFD. Nine common key characteristic flavor compounds of dried
H. marmoreus were screened using relative odor activity values (ROAV > 1), including ethyl 3-methylbutanoate, acetic acid, 2-methylbutanal, propanal, methyl 2-propenyl sulfate, trimethylamine, 3-octanone, acetaldehide, and thiophene. In the odor description of volatile compounds with ROAV > 0.1, it was found that important flavor components such as trimethylamine, 3-octanone, (
E)-2-octenal, and dimethyl disulfide are related to the aroma of seafood. Their ROAV order is HFD > UFD > HPD > HAD, indicating that
H. marmoreus using the HFD method have the strongest seafood flavor. The research findings provide theoretical guidance for selecting drying methods and refining the processing of
H. marmoreus.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT