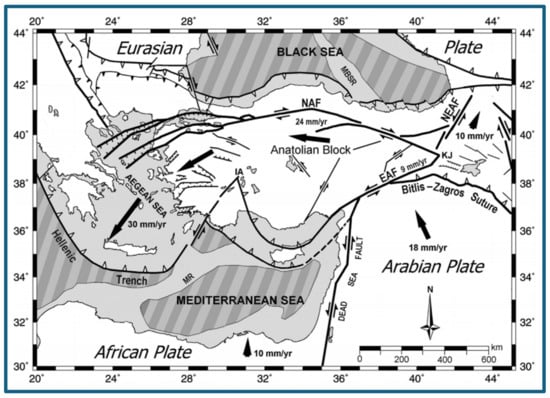
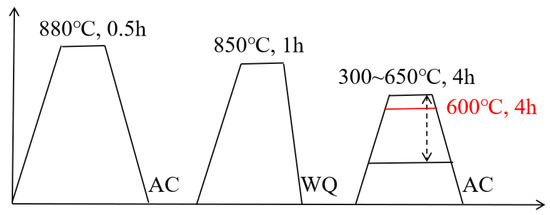
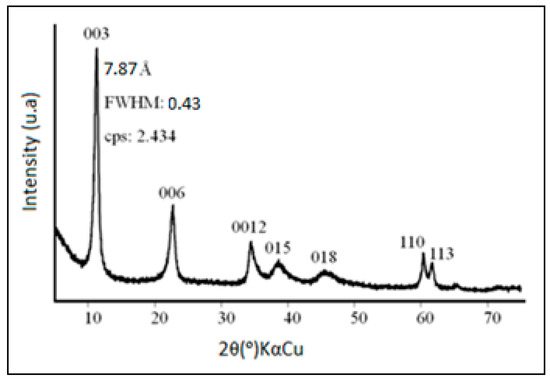
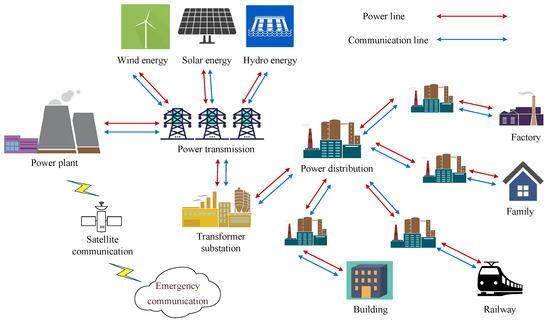
Background: Participation in targeted screening reduces lung cancer mortality by 30–60%, but screening is not universally available. Therefore, the study aimed to synthesize the evidence and identify facilitators and barriers to lung cancer screening participation globally.
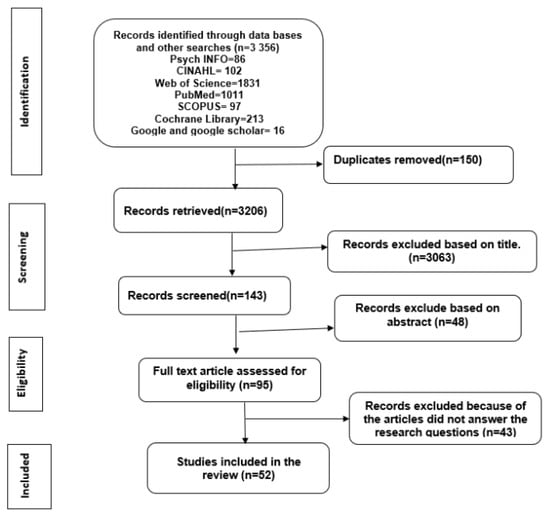
Methods: Two reviewers screened primary studies using qualitative methods published up to February 2023. We used two-phase synthesis consistent with a meta-study methodology to create an interpretation of lung cancer screening decisions grounded in primary studies, carried out a thematic analysis of group themes as specific facilitators and barriers, systematically compared investigations for similarities and differences, and performed meta-synthesis to generate an expanded theory of lung cancer screening participation. We used the Social Ecological Model to organize and interpret the themes: individual, interpersonal, social/cultural, and organizational/structural levels.
Results: Fifty-two articles met the final inclusion criteria. Themes identified as facilitating lung cancer screening included prioritizing patient education, quality of communication, and quality of provider-initiated encounter/coordination of care (individual patient and provider level), quality of the patient–provider relationship (interpersonal group), perception of a life’s value and purpose (cultural status), quality of tools designed, and care coordination (and organizational level). Themes coded as barriers included low awareness, fear of cancer diagnosis, low perceived benefit, high perceived risk of low-dose computerized tomography, concern about cancer itself, practical obstacle, futility, stigma, lack of family support, COVID-19 fear, disruptions in cancer care due to COVID-19, inadequate knowledge of care providers, shared decision, and inadequate time (individual level), patient misunderstanding, poor rapport, provider recommendation, lack of established relationship, and confusing decision aid tools (interpersonal group), distrust in the service, fatalistic beliefs, and perception of aging (cultural level), and lack of institutional policy, lack of care coordinators, inadequate infrastructure, absence of insurance coverage, and costs (and organizational status).
Conclusions: This study identified critical barriers, facilitators, and implications to lung cancer screening participation. Therefore, we employed strategies for a new digital medicine (artificial intelligence) screening method to balance the cost–benefit, “workdays” lost in case of disease, and family hardship, which is essential to improve lung cancer screening uptake.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT