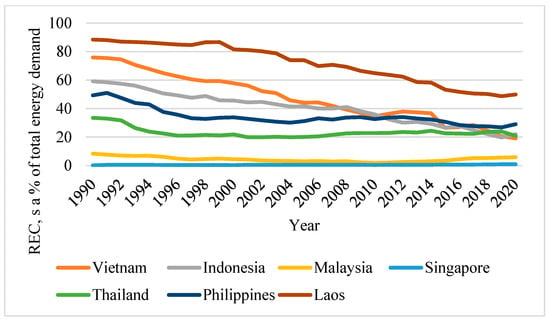
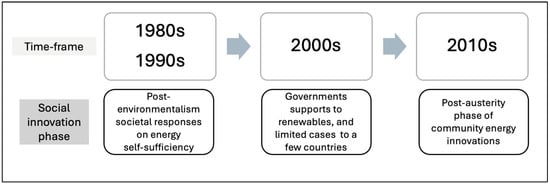
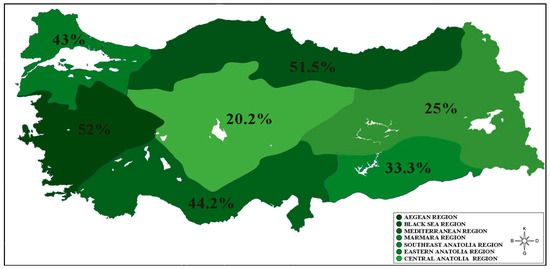
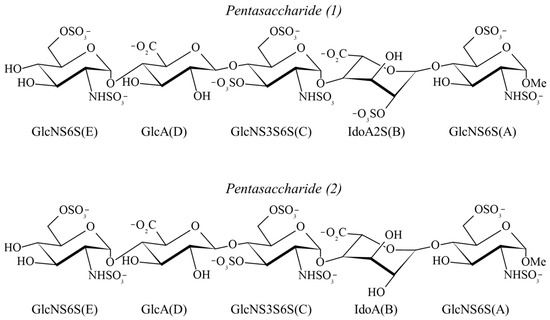
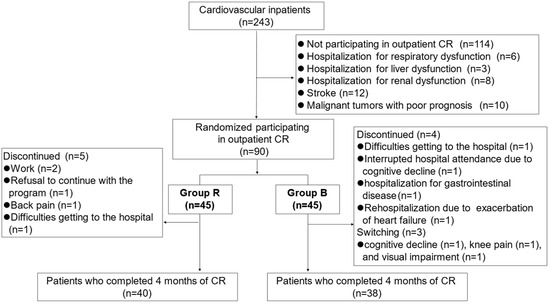
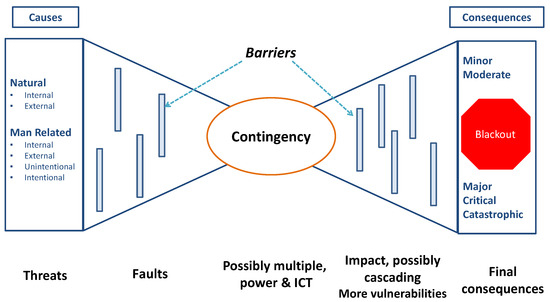
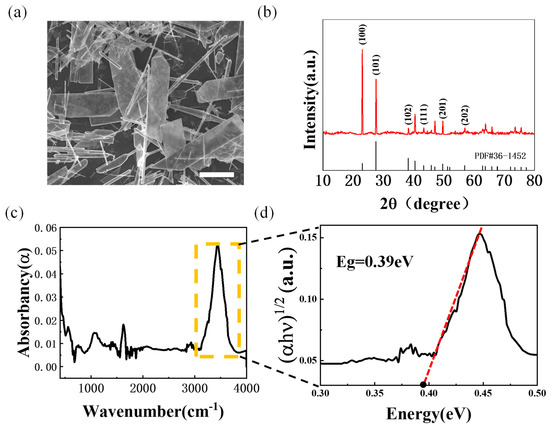
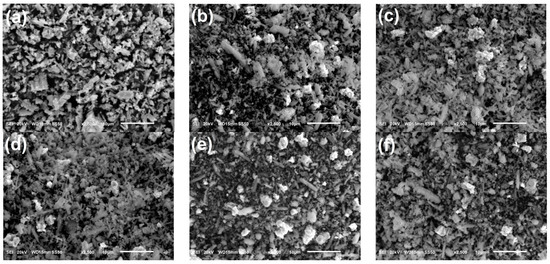
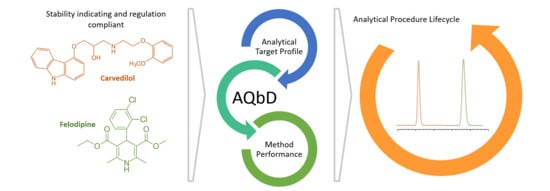
Based on the previous work conducted by Fujii et al., NdBaInO
4 compounds present modest oxide-ion conductivities. Therefore, it has been an attractive system of significant interest. In this study, we attempted to partially substitute Ca for Nd and the total electrical conductivity
[...] Read more.
Based on the previous work conducted by Fujii et al., NdBaInO
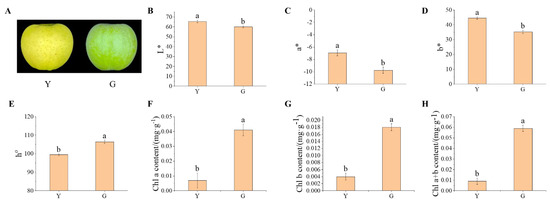
4 compounds present modest oxide-ion conductivities. Therefore, it has been an attractive system of significant interest. In this study, we attempted to partially substitute Ca for Nd and the total electrical conductivity was successfully improved due to the generation of oxygen vacancies. The synthesis, crystal structure, density, surface topography, and electrical properties of NdBaInO
4 and Ca-doped NdBaInO
4 have been studied, respectively. NdBaInO
4 and 10% and 20% molar fractions of Ca-doped NdBaInO
4 were synthesized through solid-state reactions. The crystal structure of them was obtained from Le Bail refinement of the XRD pattern, giving the result of the monoclinic structure, which belongs to P2
1/
c space group. The highest total electrical conductivity of 4.91 × 10
−3 S cm
−1 was obtained in the Nd
0.9Ca
0.1BaInO
3.95 sample at a temperature of 760 °C in the dry atmosphere and the activation energy was reduced from 0.68 eV to 0.58 eV when the temperature was above 464 °C (737 K) after doping the NdBaInO
4 with a 0.1 molar fraction of Ca
2+. Moreover, the total conductivity of Nd
0.9Ca
0.1BaInO
3.95 in the wet atmosphere at moderate temperature was relatively higher than that in the dry atmosphere, which suggests that potential proton conduction may exist in wet atmospheres. In addition, the oxygen diffusion coefficients of Nd
0.9Ca
0.1BaInO
3.95 (D* = 1.82 × 10
−8 cm
2/s, 850 °C) was about two times higher than that of Nd
0.8Ca
0.2BaInO
3.90 (D* = 7.95 × 10
−9 cm
2/s, 850 °C) and was increased significantly by two orders of magnitude when compared with the oxygen diffusion coefficient of the undoped NdBaInO
4 (D* = 8.25 × 10
−11 cm
2/s, 850 °C).
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT