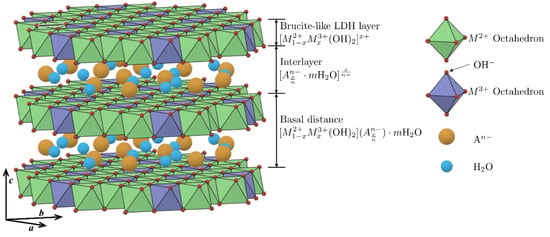
The aim of this study is to analyze the effect of the addition of TiO
2 nanoparticles (NTs) on the physical and mechanical properties, as well as the microstructural changes, of cementitious composites containing partially substituted natural aggregates (NAs) with aggregates derived from
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study is to analyze the effect of the addition of TiO
2 nanoparticles (NTs) on the physical and mechanical properties, as well as the microstructural changes, of cementitious composites containing partially substituted natural aggregates (NAs) with aggregates derived from the following four recycled materials: glass (RGA), brick (RGB), blast-furnace slag (GBA), and recycled textolite waste with WEEE (waste from electrical and electronic equipment) as the primary source (RTA), in line with sustainable construction practices. The research methodology included the following phases: selection and characterization of raw materials, formulation design, experimental preparation and testing of specimens using standardized methods specific to cementitious composite mortars (including determination of apparent density in the hardened state, mechanical strength in compression, flexure, and abrasion, and water absorption by capillarity), and structural analysis using specialized techniques (scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS)). The analysis and interpretation of the results focused primarily on identifying the effects of NT addition on the composites. Results show a decrease in density resulting from replacing NAs with recycled aggregates, particularly in the case of RGB and RTA. Conversely, the introduction of TiO
2 nanoparticles resulted in a slight increase in density, ranging from 0.2% for RTA to 7.4% for samples containing NAs. Additionally, the introduction of TiO
2 contributes to improved compressive strength, especially in samples containing RTA, while flexural strength benefits from a 3–4% TiO
2 addition in all composites. The compressive strength ranged from 35.19 to 70.13 N/mm
2, while the flexural strength ranged from 8.4 to 10.47 N/mm
2. The abrasion loss varied between 2.4% and 5.71%, and the water absorption coefficient varied between 0.03 and 0.37 kg/m
2m
0.5, the variations being influenced by both the nature of the aggregates and the amount of NTs added. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) analysis showed that TiO
2 nanoparticles are uniformly distributed in the cementitious composites, mainly forming CSH gel. TiO
2 nanoparticles act as nucleating agents during early hydration, as confirmed by EDS spectra after curing.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT