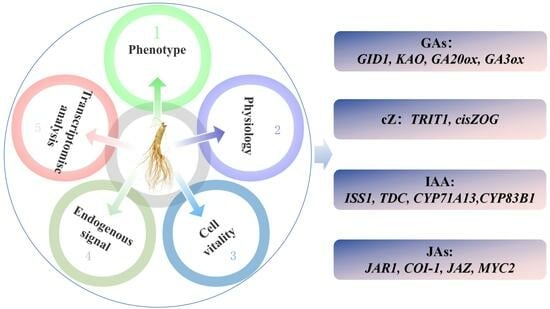
Background: Pharmacogenomic knowledge as a biomarker for cancer care has transformed clinical practice, however, as current guidelines are primarily derived from Eurocentric populations, this limits their application in Latin America, particularly among Hispanic or Latino groups. Despite advancements, systemic chemotherapy still poses challenges
[...] Read more.
Background: Pharmacogenomic knowledge as a biomarker for cancer care has transformed clinical practice, however, as current guidelines are primarily derived from Eurocentric populations, this limits their application in Latin America, particularly among Hispanic or Latino groups. Despite advancements, systemic chemotherapy still poses challenges in drug toxicity and suboptimal response. This study explores pharmacogenetic markers related to anticancer drugs in a Chilean cohort, filling a gap in Latin American research. Notably, the influence of native South American Mapuche-Huilliche ancestry. Methods: To explore pharmacogenetic markers related to anticancer drugs, we utilized an ethnically Admixed Chilean genome-wide association studies (GWAS) dataset of 1095 unrelated individuals. Pharmacogenomic markers were selected from PharmGKB, totaling 36 level 1 and 2 evidence single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and 571 level 3 SNPs. Comparative analyses involved assessing SNP frequencies across diverse populations from the 1000 Genomes Project. Haplotypes were estimated, and linkage disequilibrium was examined. Ancestry-based association analyses explored relationships between SNPs and Mapuche-Huilliche and European ancestries. Chi-square distribution with
p ≤ 0.05 and Bonferroni’s multiple adjustment tests determined statistical differences between allele frequencies. Results: Our study reveals significant disparities in SNP frequency within the Chilean population. Notably, dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase (
DPYD) variants (rs75017182 and rs67376798), linked to an increased risk of severe fluoropyrimidine toxicity, exhibit an exceptionally low frequency (minor allele frequency (MAF) < 0.005). Nudix hydrolase 15 (
NUDT15) rs116855232, associated with hematological mercaptopurine toxicity, is relatively common (MAF = 0.062), and is further linked to Mapuche-Huilliche ancestry. Thiopurine methyltransferase enzyme (TPMT), implicated in severe toxicity to mercaptopurines, SNPs rs1142345 and rs1800460 of
TMPT gene demonstrate higher MAFs in Admixed Americans and the Chilean population (MAF range 0.031–0.057). Finally, the variant in the UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1 gene (
UGT1A1) rs4148323, correlated with irinotecan neutropenia, exhibits the highest MAF in East Asian (MAF = 0.136) and Chilean (MAF = 0.025) populations, distinguishing them from other investigated populations. Conclusions: This study provides the first comprehensive pharmacogenetic characterization of cancer therapy-related SNPs and highlights significant disparities in SNP frequencies within the Chilean population. Our findings underscore the necessity for inclusive research and personalized therapeutic strategies to ensure the equitable and effective application of precision medicine across diverse global communities.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT