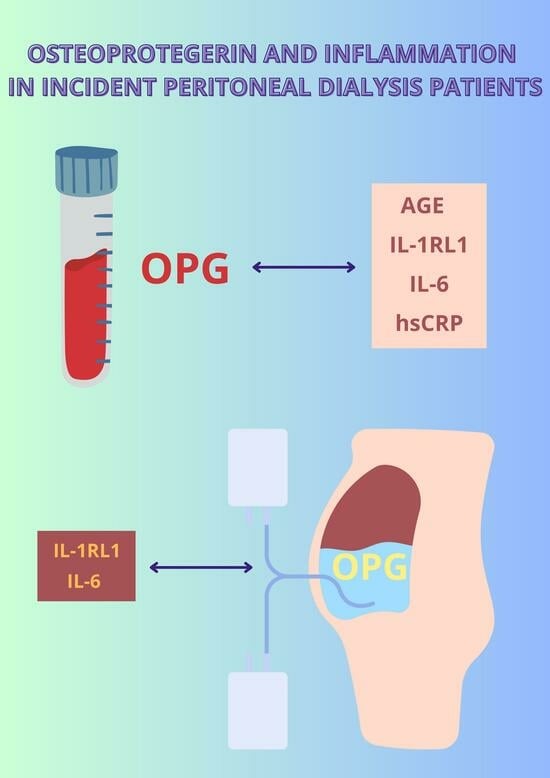
Objectives: Osteoprotegerin (OPG) is a member of the tumor necrosis factor receptor family involved in processes in many inflammatory states. OPG concentration is enhanced in the majority of chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients and those undergoing renal replacement therapy. The aim of the study was to assess the relation of OPG and chronic inflammation in peritoneal dialysis (PD) patients and to evaluate whether OPG concentrations in plasma and dialysate were related to plasma and dialysate levels of proinflammatory mediators (interleukin 6 (IL-6), high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), interleukin 33 (IL-33) and interleukin 1 receptor-like 1IL-1RL1 (IL-1RL1, sST2)).
Methods: The study included 37 patients of the Peritoneal Dialysis Center, Department of Nephrology, Transplantology and Internal Medicine, Szczecin, Poland, 4–6 weeks after the onset of peritoneal dialysis therapy. During a peritoneal equilibration test, plasma (at 2 h) and dialysate (at 4 h) OPG, IL-33, 1IL-1RL1 (sST2), IL-6 and hsCRP concentrations were determined.
Results: Plasma concentration of OPG did not correlate with dialysate OPG level (
Rs = 0.04,
p = 0.8). There was a strong positive correlation between plasma OPG concentrations and plasma IL-1RL1 (sST2) (
Rs = 0.41;
p = 0.01), plasma IL-6 (
Rs = 0.38;
p = 0.01) and plasma hsCRP (
Rs = 0.35;
p = 0.02). Dialysate OPG concentrations were positively associated with dialysate IL-1RL1 (sST2) (
Rs = 0.37;
p = 0.02) and dialysate IL-6 levels (
Rs = 0.44;
p = 0.005). Multivariate analysis showed that higher IL-1RL1 (sST2) (
ß = +0.38,
p = 0.006), higher plasma hsCRP (
ß = +0.32,
p = 0.02) and older age (
ß = +0.35,
p = 0.01) were independent determinants of higher plasma OPG concentration and that higher concentrations of dialysate IL-6 (
ß = +0.37,
p = 0.02) were independent determinants of higher dialysate OPG concentration.
Conclusions: Both plasma and dialysate OPG levels are associated with the severity of systemic and local inflammation illustrated by the plasma and dialysate concentrations of IL-1RL1 (sST2), hsCRP and IL-6, suggesting that OPG might have a pivotal role in explaining the milieu of systemic and intraperitoneal inflammation.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT