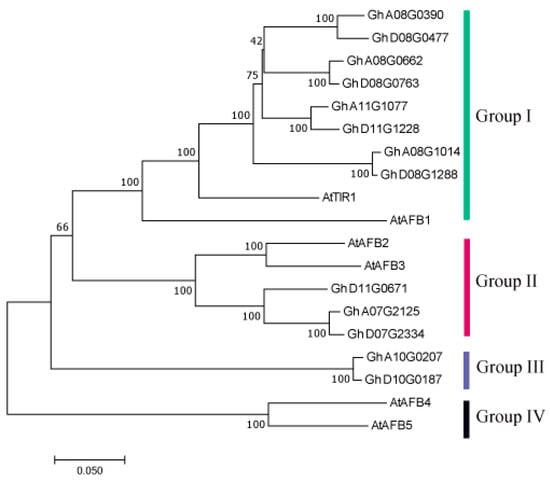
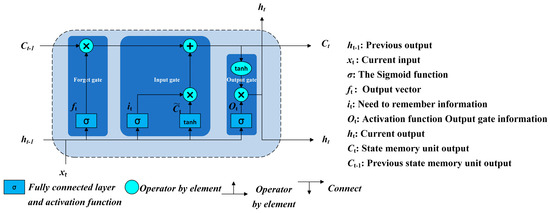
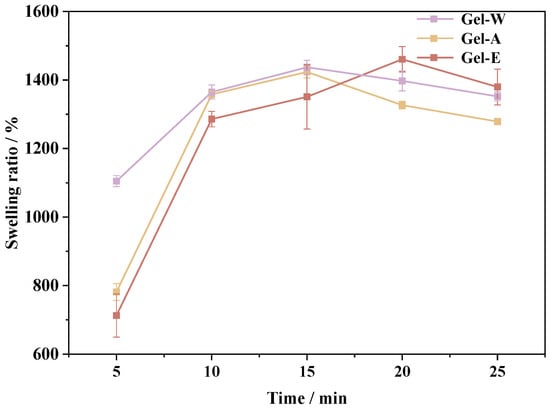
L-carnitine (LC), a vital nutritional supplement, plays a crucial role in myocardial health and exhibits significant cardioprotective effects. LC, being the principal constituent of clinical-grade supplements, finds extensive application in the recovery and treatment of diverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disorders. However, controversies persist
[...] Read more.
L-carnitine (LC), a vital nutritional supplement, plays a crucial role in myocardial health and exhibits significant cardioprotective effects. LC, being the principal constituent of clinical-grade supplements, finds extensive application in the recovery and treatment of diverse cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disorders. However, controversies persist regarding the utilization of LC in nervous system diseases, with varying effects observed across numerous mental and neurological disorders. This article primarily aims to gather and analyze database information to comprehensively summarize the therapeutic potential of LC in patients suffering from nervous system diseases while providing valuable references for further research.
Methods: A comprehensive search was conducted in PubMed, Web Of Science, Embase, Ovid Medline, Cochrane Library and Clinicaltrials.gov databases. The literature pertaining to the impact of LC supplementation on neurological or psychiatric disorders in patients was reviewed up until November 2023. No language or temporal restrictions were imposed on the search.
Results: A total of 1479 articles were retrieved, and after the removal of duplicates through both automated and manual exclusion processes, 962 articles remained. Subsequently, a meticulous re-screening led to the identification of 60 relevant articles. Among these, there were 12 publications focusing on hepatic encephalopathy (HE), while neurodegenerative diseases (NDs) and peripheral nervous system diseases (PNSDs) were represented by 9 and 6 articles, respectively. Additionally, stroke was addressed in five publications, whereas Raynaud’s syndrome (RS) and cognitive disorder (CD) each had three dedicated studies. Furthermore, migraine, depression, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) each accounted for two publications. Lastly, one article was found for other symptoms under investigation.
Conclusion: In summary, LC has demonstrated favorable therapeutic effects in the management of HE, Alzheimer’s disease (AD), carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS), CD, migraine, neurofibromatosis (NF), PNSDs, RS, and stroke. However, its efficacy appears to be relatively limited in conditions such as ALS, ataxia, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), depression, chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS), Down syndrome (DS), and sciatica.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT