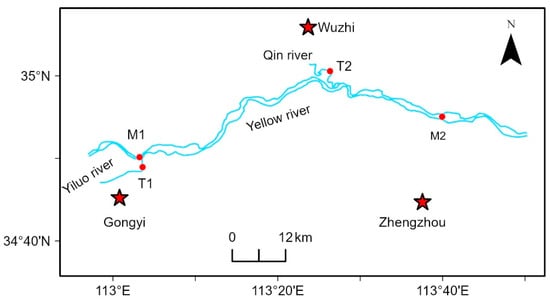
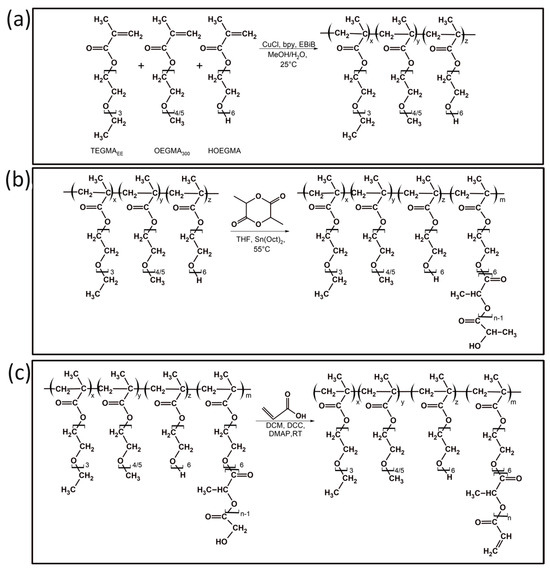
The purpose of this study was to characterize in detail the reproductive strategy, course of embryogenesis, and development of larvae in three species of fishes of the genus
Cichlasoma: the green terror (
Andinoacara rivulatus), the red discus (
Symphysodon discus), and the jaguar cichlid (
Parachromis managuensis). Eggs for the study were obtained from five pairs of each species (300 eggs from each female) and incubated at 26 °C. The developing eggs were observed under a microscope (Carl Zeiss Stereo Discovery. V12 and Nikon 2000SE software (NIS-Elements F 4.30.01 64-bit) from fertilization to larval hatching until complete yolk-sac resorption. The largest average number of eggs per female was found in the jaguar cichlid (
= 2991 eggs), a smaller average number of eggs was shown in the green terror (
= 922 eggs), and the red discus showed the smallest average number of eggs (
= 300 eggs). There were significant differences in the sizes of the eggs of the studied species: jaguar cichlid eggs were the smallest (1.060 ± 0.05 mm
3), red discus eggs were larger (1.070 ± 0.07 mm
3), and green terror eggs were the largest (1.365 ± 0.16 mm
3). The embryogenesis time in the red discus was 2132 °H (82 Hpf), in the green terror it was 2158 °H (83 Hpf), and the longest in the jaguar cichlid was 2470 °H (87 Hpf). At the end of embryogenesis, the average size of the larvae after hatching was measured (red discus
= 4.346 mm, green terror
= 5.203 mm, and jaguar cichlid
= 5.301 mm) and the time of yolk-sac resorption from the moment of hatching to the transition from endogenous to exogenous feeding was determined (jaguar cichlid 5 days, green terror 6 days, and red discus 3 days). The results of this study may contribute to the development of reproductive biotechnology for the studied fishes that could be used in aquaculture and, thus, help protect them in their natural habitats.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT