Background and Objectives: The pancreas, ensconced within the abdominal cavity, requires a plethora of sophisticated imaging modalities for its comprehensive evaluation, with ultrasonography serving as a primary investigative technique. A myriad of pancreatic pathologies, encompassing pancreatic neoplasia and a spectrum of inflammatory
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The pancreas, ensconced within the abdominal cavity, requires a plethora of sophisticated imaging modalities for its comprehensive evaluation, with ultrasonography serving as a primary investigative technique. A myriad of pancreatic pathologies, encompassing pancreatic neoplasia and a spectrum of inflammatory diseases, are detectable through these imaging strategies. Nevertheless, the intricate anatomical confluence and the pancreas’s deep-seated topography render the visualization and accurate diagnosis of its pathologies a formidable endeavor. The objective of our paper is to review the best diagnostic imagistic tools for the pancreas.
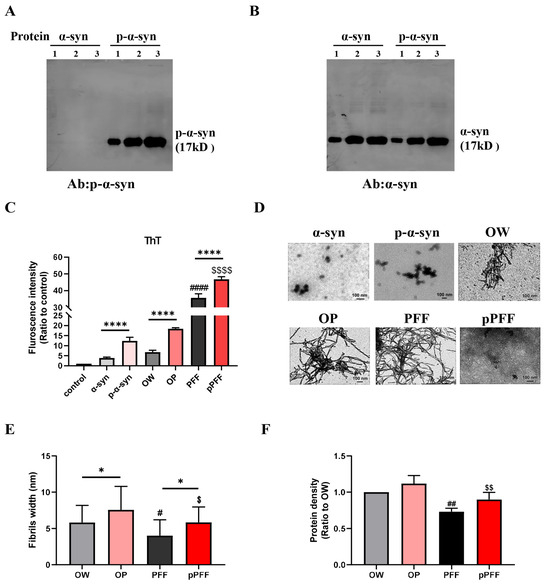
Materials and Methods: we have gathered several articles using Prisma guidelines to determine the best imagistic methods. The imperative of pancreatic scanning transcends its diagnostic utility, proving to be a pivotal element in a multitude of clinical specialties, notably surgical oncology. Within this domain, multidetector computed tomography (MDCT) of the pancreas holds the distinction of being the paramount imaging modality, endorsed for its unrivaled capacity to delineate the staging and progression of pancreatic carcinoma. In synergy with MDCT, there has been a notable advent of avant-garde imaging techniques in recent years. These advanced methodologies, including ultrasonography, endoscopic ultrasonography, contrast-enhanced ultrasonography, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) conjoined with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP), have broadened the horizon of tumor characterization, offering unparalleled depth and precision in oncological assessment. Other emerging diagnostic techniques, such as elastography, also hold a lot of potential and promise for the future of pancreatic imaging. Fine needle aspiration (FNA) is a quick, minimally invasive procedure to evaluate lumps using a thin needle to extract tissue for analysis. It is less invasive than surgical biopsies and usually performed as an outpatient with quick recovery. Its accuracy depends on sample quality, and the risks include minimal bleeding or discomfort. Results, guiding further treatment, are typically available within a week. Elastography is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that maps the elastic properties and stiffness of soft tissue. This method, often used in conjunction with ultrasound or MRI, helps differentiate between hard and soft areas in tissue, providing valuable diagnostic information. It is particularly useful for assessing liver fibrosis, thyroid nodules, breast lumps, and musculoskeletal conditions. The technique is painless and involves applying gentle pressure to the area being examined. The resulting images show tissue stiffness, indicating potential abnormalities. Elastography is advantageous for its ability to detect diseases in early stages and monitor treatment effectiveness. The procedure is quick, safe, and requires no special preparation, with results typically available immediately.
Results: The assembled and gathered data shows the efficacy of various techniques in discerning the nature and extent of neoplastic lesions within the pancreas.
Conclusions: The most common imaging modalities currently used in diagnosing pancreatic neoplasms are multidetector computed tomography (MDCT), endoscopic ultrasound (EUS), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), alongside new technologies, such as elastography.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT