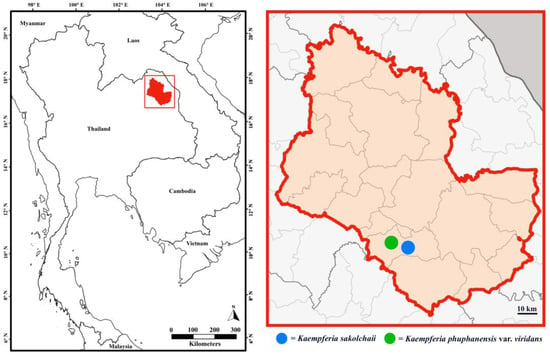
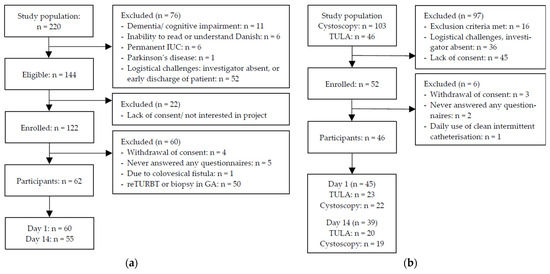
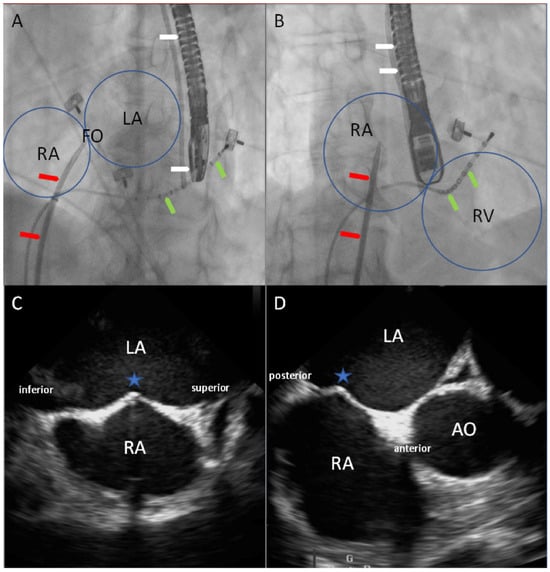
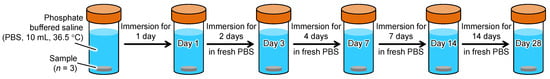
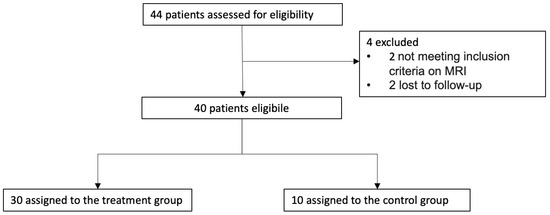
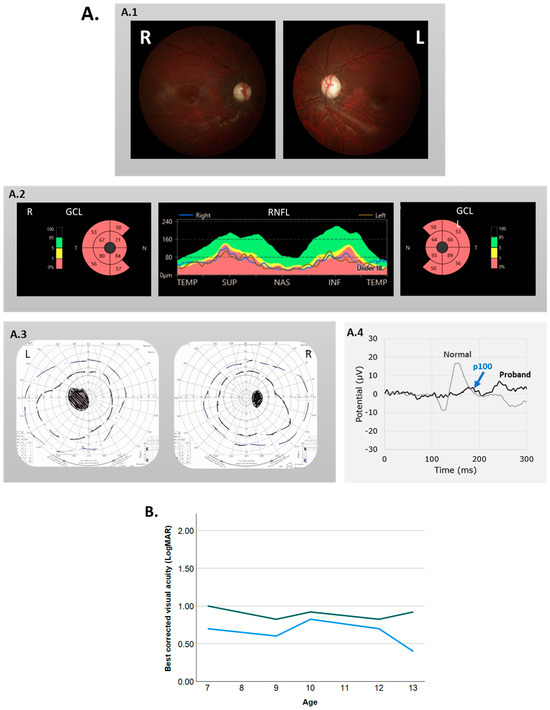
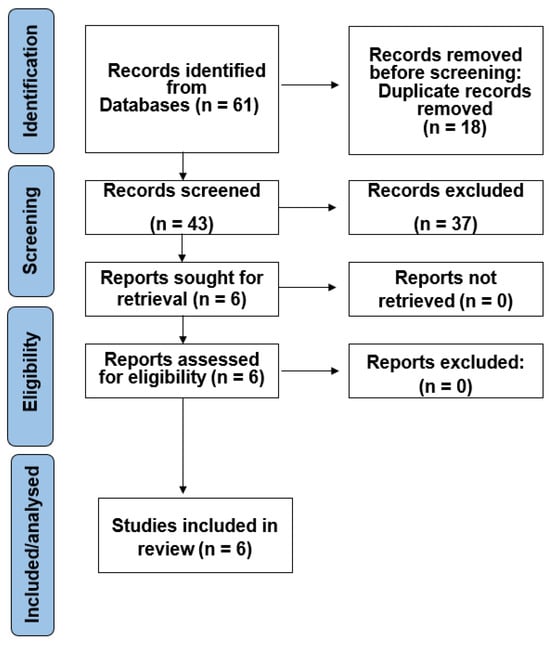
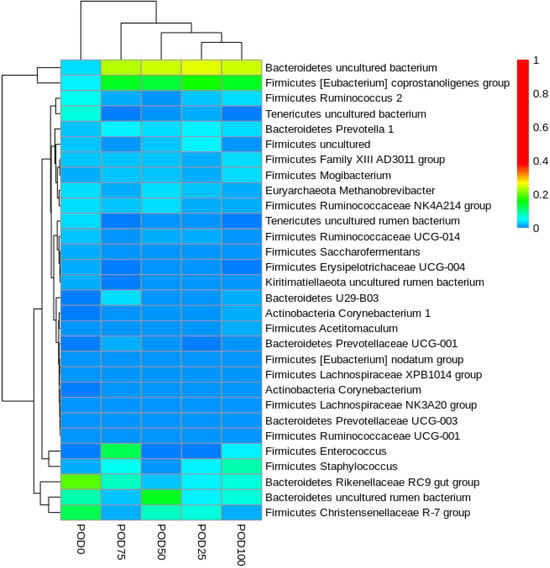
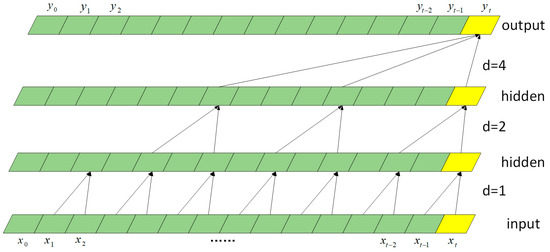
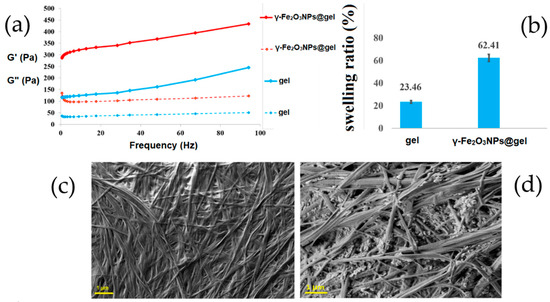
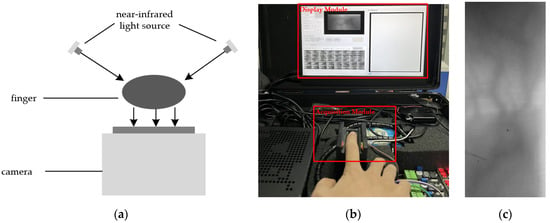
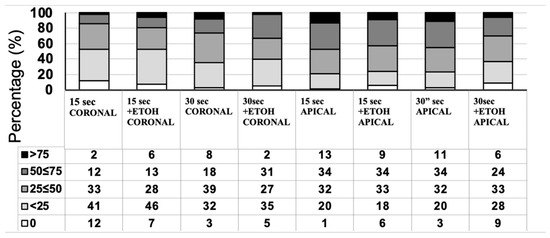
The objective of this study was to investigate how nitrogen and slow-release fertilizers affect the traits of leaf senescence and quinoa production in order to explore the optimal slow-release fertilizer and nitrogen fertilizer ratios suitable for quinoa production, as well as to provide theoretical references for the planting of quinoa fertilization methods and fertilizer amount. In this experiment, the main local strain Quinoa 77 was selected as the experimental material, and six treatments were set up: CK: no nitrogen fertilizer; T
1: 100% urea (N); T
2: 100% slow-release fertilizer (C); T
3: 5:5 (C
5N
5); T
4: 3:7 (C
3N
7); and T
5: 7:3 (C
7N
3). This was done in order to investigate how various treatments affect the activities of catalase (CAT), peroxidase (POD), and superoxide dismutase (SOD); malondialdehyde (MDA) content; and yield of quinoa leaves. The findings revealed the following: (1) As the reproductive period progressed, the activities of CAT, POD, and SOD in quinoa leaves treated differently showed a tendency to increase and subsequently decrease, and they reached the peak value at the early stage of filling. The activity of CAT, POD, and SOD in the T
3 treatment was the highest, and the average activities were 3148.74 U·g
−1, 2197.84 U·g
−1, and 118.51 U·g
−1, respectively, which increased by 78.90%, 101.99%, and 108.14%, respectively, compared with CK. The content of MDA continued to increase with the progress of fertility. The average T
3 treatment was 36.41 nmol·g
−1, which was 46.87% lower than that of CK. (2) Out of all the treatments, T
3 had the highest yield with an average of 3829.43 kg·hm
−2, T
5 the second with an average of 3313.52 kg·hm
−2, and T
4 the third with 2847.47 kg·hm
−2, which increased yields by 96.18%, 69.75%, and 45.87%, respectively, compared with CK. (3) Yield was highly significantly and positively correlated with thousand kernel weight; number of grains per spike per plant; and the early filling stages of CAT, POD, and SOD sports, and it had a negative, extremely significant correlation with MDA content. Comprehensive analysis showed that slow-release fertilizer and nitrogen fertilizer can improve the antioxidant enzyme activity of quinoa leaves, inhibit MDA content, improve the physiological characteristics of quinoa, and delay the purpose of leaf senescence, with a better effect of yield and income, of which the T
3 treatment had the high-quality impact of increasing yields and was a more scientific and reasonable fertilization method.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT