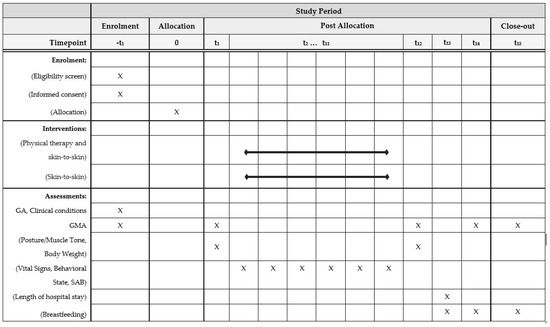
Background: to examine factors associated with cardiac evaluation and associations between cardiac test abnormalities and clinical outcomes in patients with acute brain injury (ABI) due to acute ischemic stroke (AIS), spontaneous subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH), spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage (sICH), and traumatic brain injury (TBI) requiring neurocritical care.
Methods: In a cohort of patients ≥18 years, we examined the utilization of electrocardiography (ECG), beta-natriuretic peptide (BNP), cardiac troponin (cTnI), and transthoracic echocardiography (TTE). We investigated the association between cTnI, BNP, sex-adjusted prolonged QTc interval, low ejection fraction (EF < 40%), all-cause mortality, death by neurologic criteria (DNC), transition to comfort measures only (CMO), and hospital discharge to home using univariable and multivariable analysis (adjusted for age, sex, race/ethnicity, insurance carrier, pre-admission cardiac disorder, ABI type, admission Glasgow Coma Scale Score, mechanical ventilation, and intracranial pressure [ICP] monitoring).
Results: The final sample comprised 11,822 patients: AIS (46.7%), sICH (18.5%), SAH (14.8%), and TBI (20.0%). A total of 63% (
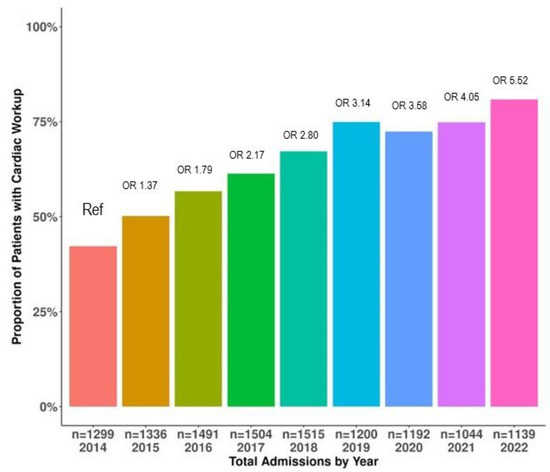
n = 7472) received cardiac workup, which increased over nine years (
p < 0.001). A cardiac investigation was associated with increased age, male sex (aOR 1.16 [1.07, 1.27]), non-white ethnicity (aOR), non-commercial insurance (aOR 1.21 [1.09, 1.33]), pre-admission cardiac disorder (aOR 1.21 [1.09, 1.34]), mechanical ventilation (aOR1.78 [1.57, 2.02]) and ICP monitoring (aOR1.68 [1.49, 1.89]). Compared to AIS, sICH (aOR 0.25 [0.22, 0.29]), SAH (aOR 0.36 [0.30, 0.43]), and TBI (aOR 0.19 [0.17, 0.24]) patients were less likely to receive cardiac investigation. Patients with troponin 25th–50th quartile (aOR 1.65 [1.10–2.47]), troponin 50th–75th quartile (aOR 1.79 [1.22–2.63]), troponin >75th quartile (aOR 2.18 [1.49–3.17]), BNP 50th-75th quartile (aOR 2.86 [1.28–6.40]), BNP >75th quartile (aOR 4.54 [2.09–9.85]), prolonged QTc (aOR 3.41 [2.28; 5.30]), and EF < 40% (aOR 2.47 [1.07; 5.14]) were more likely to be DNC. Patients with troponin 50th–75th quartile (aOR 1.77 [1.14–2.73]), troponin >75th quartile (aOR 1.81 [1.18–2.78]), and prolonged QTc (aOR 1.71 [1.39; 2.12]) were more likely to be associated with a transition to CMO. Patients with prolonged QTc (aOR 0.66 [0.58; 0.76]) were less likely to be discharged home.
Conclusions: This large, single-center study demonstrates low rates of cardiac evaluations in TBI, SAH, and sICH compared to AIS. However, there are strong associations between electrocardiography, biomarkers of cardiac injury and heart failure, and echocardiography findings on clinical outcomes in patients with ABI. Findings need validation in a multicenter cohort.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT