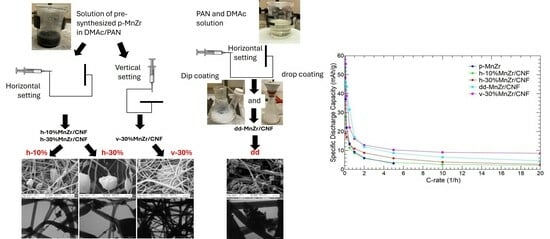
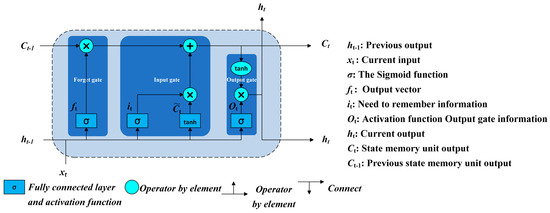
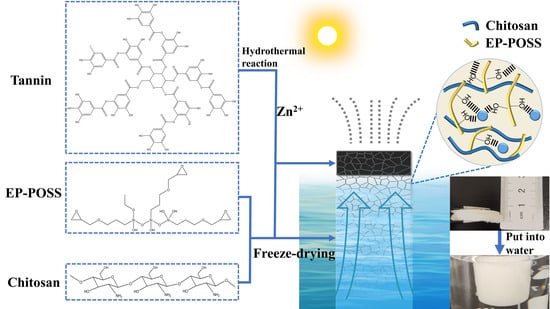
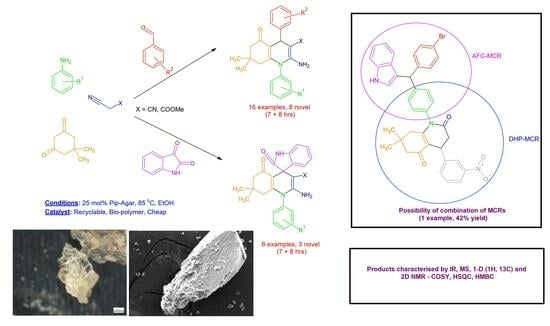
The NASICON-structured Na
3MnZr(PO
4)
3 compound is a promising high-voltage cathode material for sodium-ion batteries (SIBs). In this study, an easy and scalable electrospinning approach was used to synthesize self-standing cathodes based on Na
3MnZr(PO
4)
3 loaded into carbon nanofibers (CNFs). Different strategies were applied to load the active material. All the employed characterization techniques (X-ray powder diffraction (XRPD), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS), thermal gravimetric analysis (TGA), and Raman spectroscopy) confirmed the successful loading. Compared to an appositely prepared tape-cast electrode, Na
3MnZr(PO
4)
3/CNF self-standing cathodes demonstrated an enhanced specific capacity, especially at high C-rates, thanks to the porous conducive carbon nanofiber matrix. Among the strategies applied to load Na
3MnZr(PO
4)
3 into the CNFs, the electrospinning (vertical setting) of the polymeric solution containing pre-synthesized Na
3MnZr(PO
4)
3 powders resulted effective in obtaining the quantitative loading of the active material and a homogeneous distribution through the sheet thickness. Notably, Na
3MnZr(PO
4)
3 aggregates connected to the CNFs, covered their surface, and were also embedded, as demonstrated by TEM and EDS. Compared to the self-standing cathodes prepared with the horizontal setting or dip–drop coating methods, the vertical binder-free electrode exhibited the highest capacity values of 78.2, 55.7, 38.8, 22.2, 16.2, 12.8, 10.3, 9.0, and 8.5 mAh/g at C-rates of 0.05C, 0.1C, 0.2C, 0.5C, 1C, 2C, 5C, 10C, and 20C, respectively, with complete capacity retention at the end of the measurements. It also exhibited a good cycling life, compared to its tape-cast counterpart: it displayed higher capacity retention at 0.2C and 1C, and, after cycling 1000 cycles at 1C, it could be further cycled at 5C, 10C, and 20C.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT