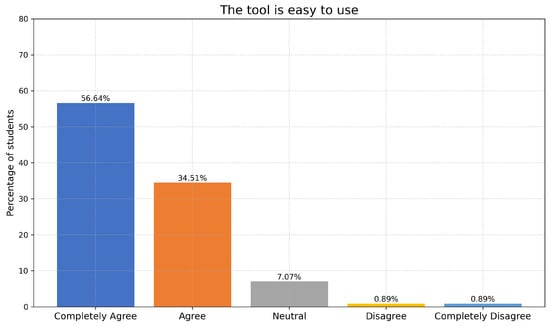
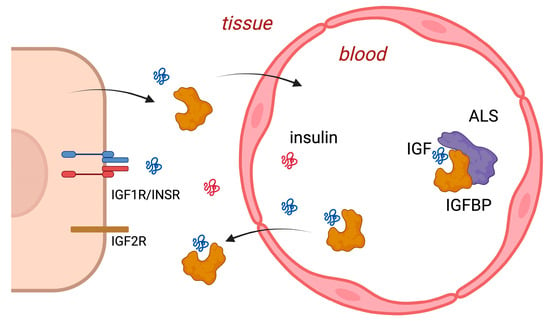
One biostrategy to boost the sustainability of strawberry cultivation is the application of biostimulants to the growing substrate. Here, we investigated whether the use of biostimulants and their combinations affects the strawberry plants’ phyllochron, phenology, and fruit quality. We tested the absence (control)
[...] Read more.
One biostrategy to boost the sustainability of strawberry cultivation is the application of biostimulants to the growing substrate. Here, we investigated whether the use of biostimulants and their combinations affects the strawberry plants’ phyllochron, phenology, and fruit quality. We tested the absence (control) and presence of biostimulants (arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF),
Ascophyllum nodosum (AN),
Trichoderma harzianum (TH), AMF + AN, AMF + TH, AN + TH, and AMF + AN + TH). The experimental design used was in completely randomized blocks (four replications). AMF was represented by a multi-species on-farm inoculant;
A. nodosum was represented by the commercial product Acadian
®; and
T. harzianum was represented by the commercial product Trichodermil
®. The leaf emission rate, the occurrence and duration of phenological stages, and fruit quality were assessed. The greatest precocity in terms of harvesting the first fruit was observed in plants grown with AMF + TH, which also had the lowest phyllochron (77.52 °C day·leaf
−1). Those treated only with AMF were the latest (144.93 °C day·leaf
−1). More flavorful fruits were produced by plants grown with AMF + TH. Plants inoculated with the AMF community, whether or not associated with
A. nodosum and
T. harzianum, had more than 94% mycorrhizal colonization. We conclude that AMF,
A. nodosum,
T. harzianum, and their combinations influence the phenology, phyllochron, and fruit quality of strawberry plants. In the growing conditions of the Brazilian subtropics, the AMF and
T. harzianum combination shortens the strawberry cycle, from transplanting the daughter plants to harvesting the first fruit, and improves the fruit flavor.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT