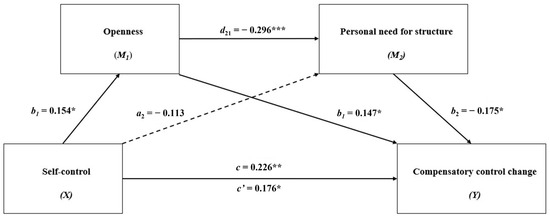
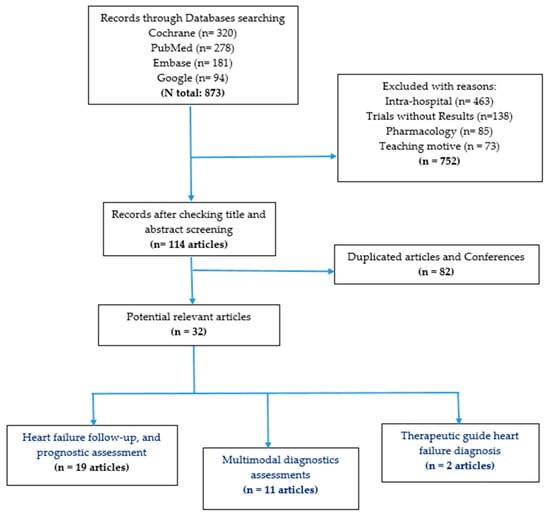
In contrast to cats and dogs, here we report that the α
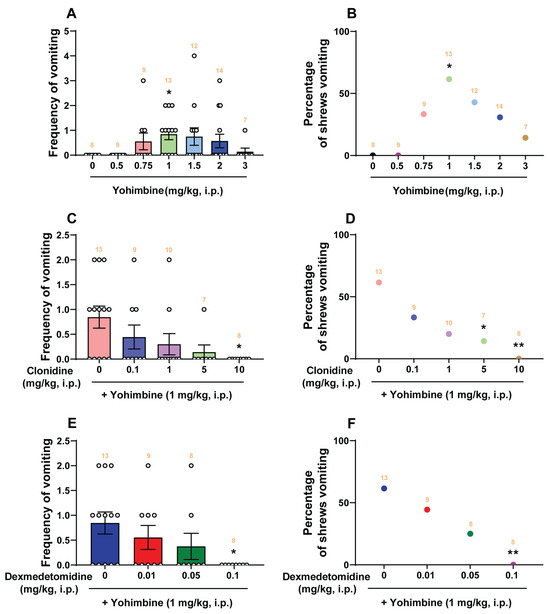
2-adrenergic receptor antagonist yohimbine is emetic and corresponding agonists clonidine and dexmedetomidine behave as antiemetics in the least shrew model of vomiting. Yohimbine (0, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.5, 2, and
[...] Read more.
In contrast to cats and dogs, here we report that the α
2-adrenergic receptor antagonist yohimbine is emetic and corresponding agonists clonidine and dexmedetomidine behave as antiemetics in the least shrew model of vomiting. Yohimbine (0, 0.5, 0.75, 1, 1.5, 2, and 3 mg/kg, i.p.) caused vomiting in shrews in a bell-shaped and dose-dependent manner, with a maximum frequency (0.85 ± 0.22) at 1 mg/kg, which was accompanied by a key central contribution as indicated by increased expression of c-
fos, serotonin and substance P release in the shrew brainstem emetic nuclei. Our comparative study in shrews demonstrates that clonidine (0, 0.1, 1, 5, and 10 mg/kg, i.p.) and dexmedetomidine (0, 0.01, 0.05, and 0.1 mg/kg, i.p.) not only suppress yohimbine (1 mg/kg, i.p.)-evoked vomiting in a dose-dependent manner, but also display broad-spectrum antiemetic effects against diverse well-known emetogens, including 2-Methyl-5-HT, GR73632, McN-A-343, quinpirole, FPL64176, SR141716A, thapsigargin, rolipram, and ZD7288. The antiemetic inhibitory ID
50 values of dexmedetomidine against the evoked emetogens are much lower than those of clonidine. At its antiemetic doses, clonidine decreased shrews’ locomotor activity parameters (distance moved and rearing), whereas dexmedetomidine did not do so. The results suggest that dexmedetomidine represents a better candidate for antiemetic potential with advantages over clonidine.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT