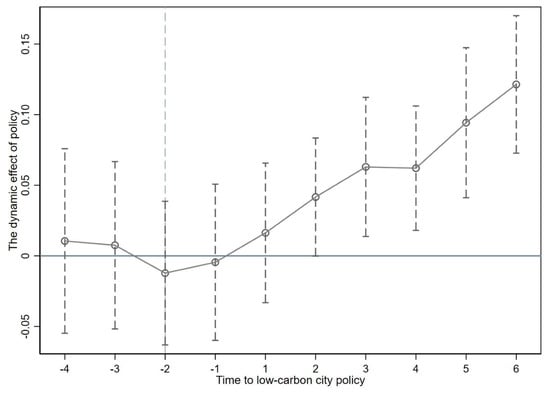
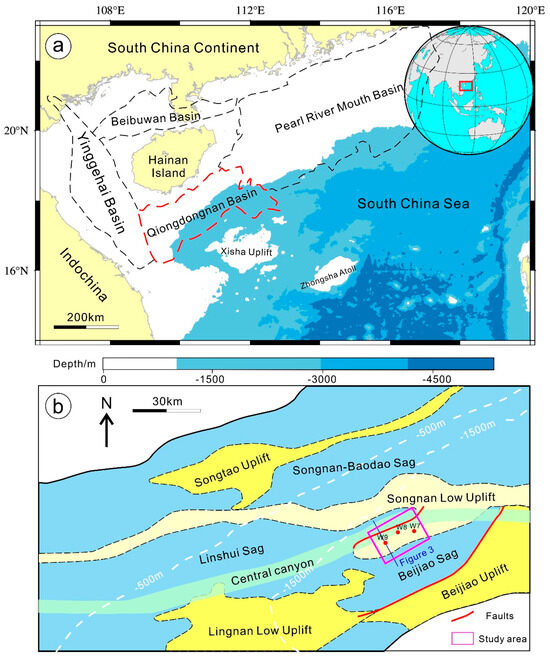
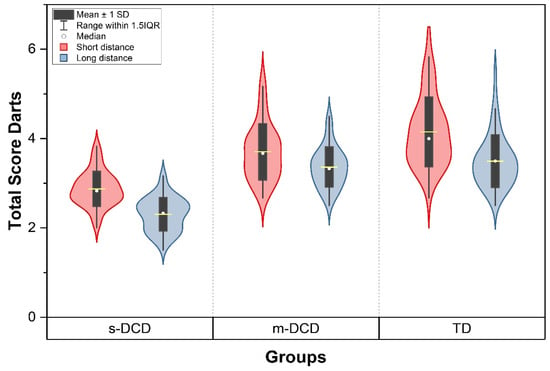
The genome of the osmophilic
Aspergillus wentii, unlike that of the osmotolerant
Aspergillus nidulans, contains only the
gfdA, but not the
gfdB, glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. Here, we studied transcriptomic changes of
A. nidulans (reference strain and Δ
gfdB
[...] Read more.
The genome of the osmophilic
Aspergillus wentii, unlike that of the osmotolerant
Aspergillus nidulans, contains only the
gfdA, but not the
gfdB, glycerol 3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene. Here, we studied transcriptomic changes of
A. nidulans (reference strain and Δ
gfdB gene deletion mutant) and
A. wentii (reference strain and
An-gfdB expressing mutant) elicited by high osmolarity.
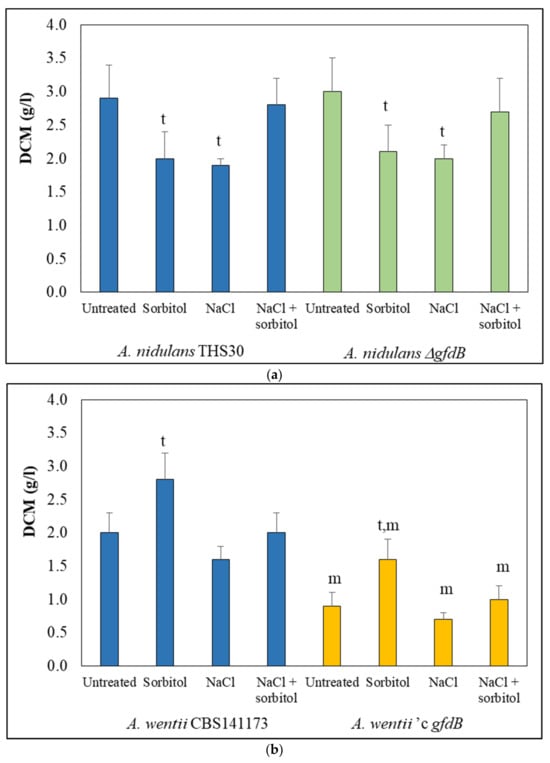
A. nidulans showed a canonic hyperosmotic stress response characterized by the upregulation of the trehalose and glycerol metabolism genes (including
gfdB), as well as the genes of the high-osmolarity glycerol (HOG) map kinase pathway. The deletion of
gfdB caused only negligible alterations in the transcriptome, suggesting that the glycerol metabolism was flexible enough to compensate for the missing GfdB activity in this species.
A. wentii responded differently to increased osmolarity than did
A. nidulans, e.g., the bulk upregulation of the glycerol and trehalose metabolism genes, along with the HOG pathway genes, was not detected. The expression of
An-gfdB in
A. wentii did not abolish osmophily, but it reduced growth and caused much bigger alterations in the transcriptome than did the missing
gfdB gene in
A. nidulans. Flexible glycerol metabolism and hence, two differently regulated
gfd genes, may be more beneficial for osmotolerant (living under changing osmolarity) than for osmophilic (living under constantly high osmolarity) species.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT