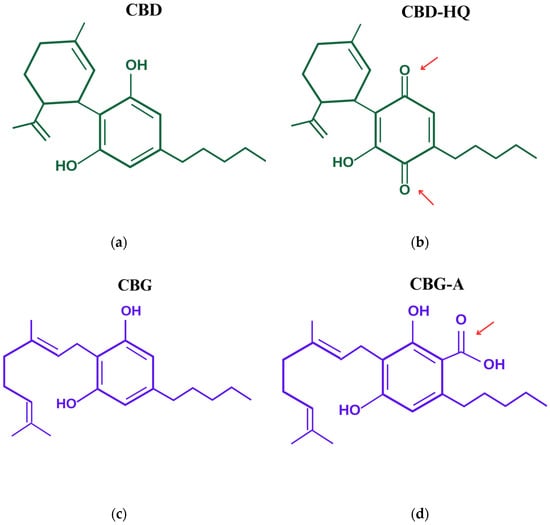
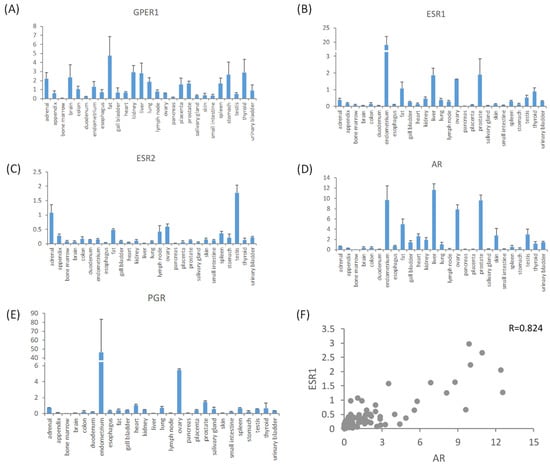
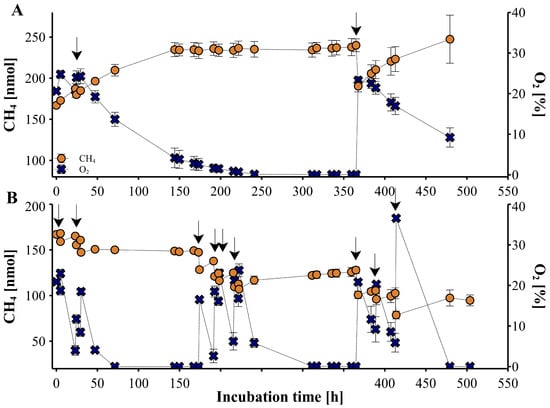
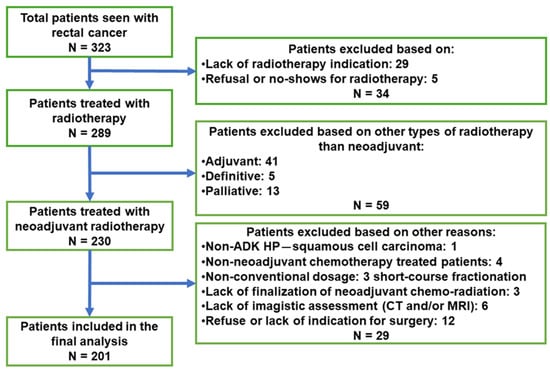
Saprotrophic fungi, key players in global carbon cycling, have been identified as methane (CH
4) sources not yet accounted for in the global CH
4 budget. This study, for the first time, explores the influence of oxygen (O
2) and temperature
[...] Read more.
Saprotrophic fungi, key players in global carbon cycling, have been identified as methane (CH
4) sources not yet accounted for in the global CH
4 budget. This study, for the first time, explores the influence of oxygen (O
2) and temperature on CH
4 production by two fungi,
Laetiporus sulphureus and
Pleurotus sapidus. To explore the relationship between these parameters and fungal CH
4 formation, we examined CH
4 formation under varying O
2 levels (0 to 98%) and temperatures (17, 27, and 40 °C) during fungal growth on pine wood, beech wood, and grass under sterile conditions. Our findings show that fungal CH
4 formation strongly depends on O
2 levels. Methane formation was highest when O
2 levels exceeded 5%, whilst no CH
4 formation was observed after complete O
2 consumption. Reintroducing O
2 immediately resumed fungal CH
4 production. Methane formation normalized to O
2 consumption (CH
4_
norm) showed a different pattern.
L. sulphureus showed higher CH
4_
norm rates with higher O
2 levels, whereas
P. sapidus showed elevated rates between 0 and 5%. Temperature also significantly influenced CH
4 and CH
4_
norm rates, with the highest production at 27 °C, and comparatively lower rates at 17 and 40 °C. These findings demonstrate the importance of O
2 levels and temperature in fungal CH
4 emissions, which are essential for refining CH
4 source predictions.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT