Background and Objectives: The neuroendocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including reproduction, with evidence suggesting its significant involvement in male fertility and sperm development. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) are expressed
[...] Read more.
Background and Objectives: The neuroendocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions, including reproduction, with evidence suggesting its significant involvement in male fertility and sperm development. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) and pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) are expressed in both male and female reproductive tissues, influencing penile erection and regulating steroidogenesis in males. Therefore, our study aimed to compare the protein levels of VIP and PACAP in seminal plasma between healthy controls and sub-fertile patients. Additionally, we sought to correlate the levels of these biomarkers with clinical, functional, and laboratory findings in the participants.
Materials and Methods: The study included a total of 163 male participants for analysis. The participants were further stratified into subgroups of fertile and sub-fertile men of four subgroups according to the 2021 WHO guidelines. Seminal plasma concentrations of the neuropeptides VIP and PACAP were measured using human enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay technique.
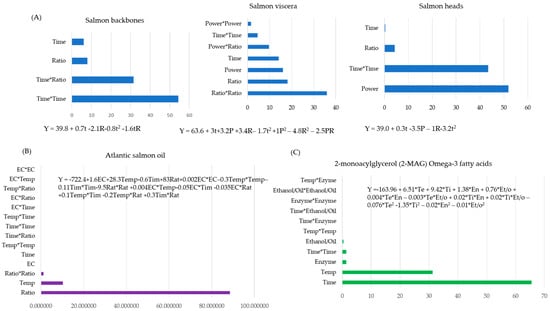
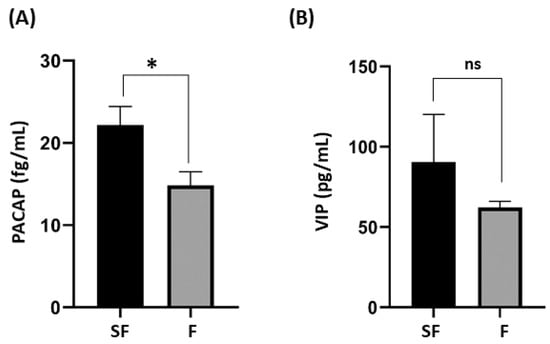
Results: The findings showed statistically significant differences in total sperm count, sperm concentration, total motility, and vitality (
p < 0.001) between the fertile group and the sub-fertile group. Specifically, significant differences found between healthy males and oligoasthenospermic patients (
p = 0.002), and between asthenospermic and oligoasthenospermic patients (
p = 0.039). An ROC analysis showed associated sensitivity and specificity values of 62.2% and 55.6%, respectively, to PACAP seminal levels differentiated between sub-fertile patients from fertile males (
p = 0.028). No significant difference in seminal levels of VIP was found between the sub-fertile and fertile groups.
Conclusions: Previous research leads to the point of PACAP active involvement in spermatogenesis. In accordance to our study, in human semen samples, we have seen a significance change in PACAP levels amongst patients with low sperm count or with both low sperm count and low motility, hinting at its contribution and acting as a possible factor in this complex process. Thus, alterations in the levels or actions of these neuropeptides have been associated with certain reproductive disorders in males.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT