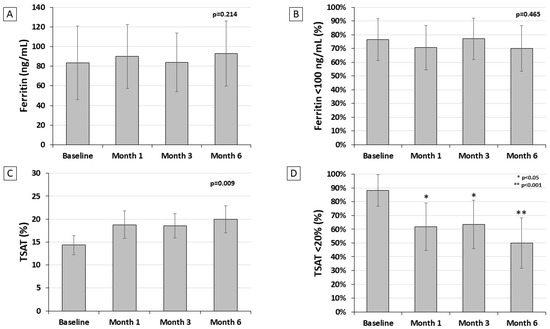
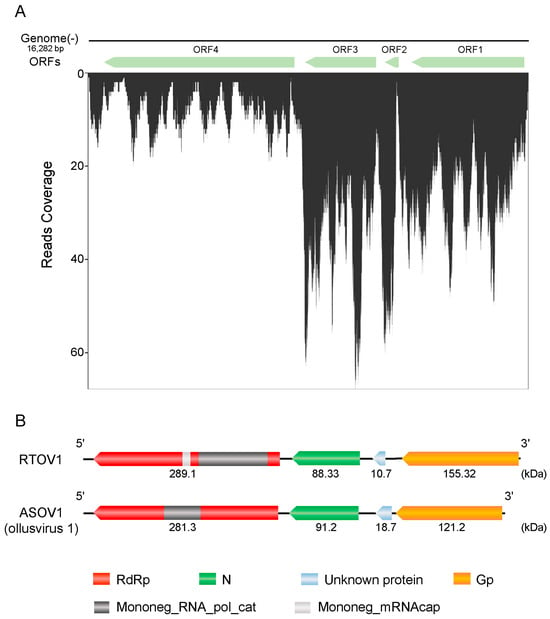
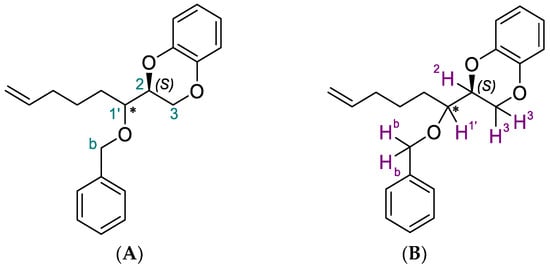
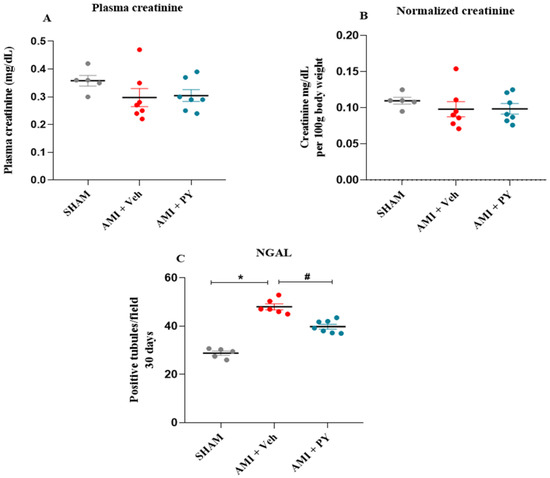
Cinmethylin is a potential pre-emergence herbicide that could be used to control grass weeds in winter cereals. To determine the herbicidal activity of cinmethylin against common gramineous weeds in wheat fields in China and its level of safety on wheat, we conducted the following experiments: (i) assessing the efficacy of cinmethylin against 11 grass weeds and (ii) determining its safety against 19 wheat varieties. The results showed that cinmethylin had good herbicidal efficacy against annual bluegrass (
Poa annua L.), shortawn foxtail (
Alopecurus aequalis Sobol.), slender meadow foxtail (
Alopecurus myosuroides Huds.), Japanese foxtail (
Alopecurus japonicus Steud.), Italian ryegrass (
Lolium multiflorum Lam.), British timothy (
Phleum paniculatum Huds.), Asia Minor bluegrass (
Polypogon fugax Nees ex Steud.),
Helictotrichon tibeticum (Roshev.) Holub., and wild oat (
Avena fatua L.), with a GR
50 (the herbicide dose resulting in 50% growth inhibition) value of 4.50–99.21 g a.i. ha
−1 in plant height and 1.43–70.34 g a.i. ha
−1 in fresh weight. However, cinmethylin cannot control Japanese brome (
Bromus japonicus L.) or Tausch’s goatgrass (
Aegilops tauschii Coss.) at a dose of 200 g a.i. ha
−1. Different wheat varieties varied in their phytotoxicity to cinmethylin. Overall, there is a phytotoxicity risk when using cinmethylin on wheat, mainly to wheat roots, with a reduction in root length of 40.81–64.09% at a dose of 400 g a.i. ha
−1. These findings indicate that the pre-emergence herbicide cinmethylin provides good efficacy against most grass weeds and may possess potential for weed management in wheat fields. However, attention should be given to the application dosage and the sensitivity of wheat varieties when using cinmethylin in wheat fields.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT