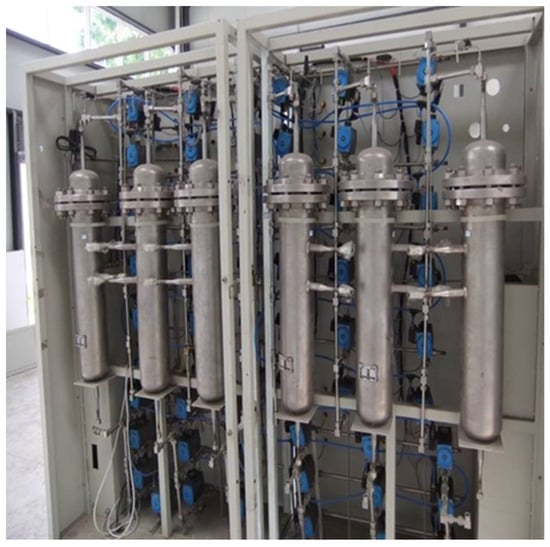
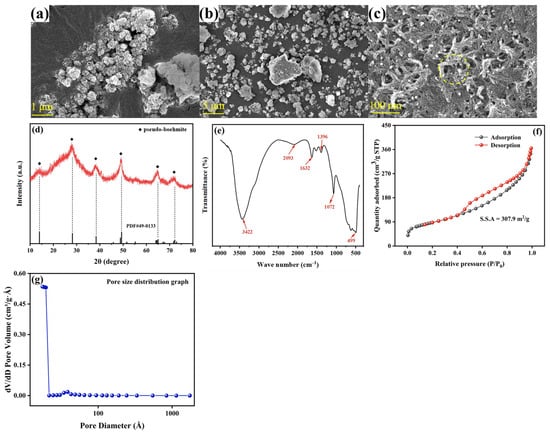
The goal of this study was to apply the principles of analytical quality by design (AQbD) to the analytical method for determining the radiochemical purity (PQR) of the radiopharmaceutical sodium iodide
131I oral solution, utilizing thin-layer chromatography (TLC) with a radio–TLC scanner,
[...] Read more.
The goal of this study was to apply the principles of analytical quality by design (AQbD) to the analytical method for determining the radiochemical purity (PQR) of the radiopharmaceutical sodium iodide
131I oral solution, utilizing thin-layer chromatography (TLC) with a radio–TLC scanner, which also enables the evaluation of product quality. For AQbD, the analytical target profile (ATP), critical quality attributes (CQA), risk management, and the method operable design region (MODR) were defined through response surface methodology to optimize the method using MINITAB
® 19 software. This study encompassed the establishment of a control strategy and the validation of the method, including the assessment of selectivity, linearity, precision, robustness, detection limit, quantification limit, range, and the stability of the sample solution. Under the experimental conditions, the method parameters of the TLC scanner were experimentally demonstrated and optimized with an injection volume of 3 µL, a radioactive concentration of 10 mCi/mL, and a carrier volume of 40 µL. Statistical analysis confirmed the method’s selectivity for the
131I iodide band Rf of 0.8, a radiochemical impurity IO
3− Rf of 0.6, a linearity from 6.0 to 22.0 mCi/mL, and an intermediate precision with a global relative standard deviation (RSD) of 0.624%. The method also exhibited robustness, with a global RSD of 0.101%, a detection limit of 0.09 mCi/mL, and a quantification limit of 0.53 Ci/mL, meeting the prescribed range and displaying stability over time (at 0, 2, and 20 h) with a global RSD of 0.362%, resulting in consistent outcomes. The development of a method based on AQbD facilitated the creation of a design space and an operational space, with comprehensive knowledge of the method’s characteristics and limitations. Additionally, throughout all operations, compliance with the acceptance criteria was verified. The method’s validity was confirmed under the established conditions, making it suitable for use in the manufacturing process of sodium iodide
131I and application in nuclear medicine services.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT