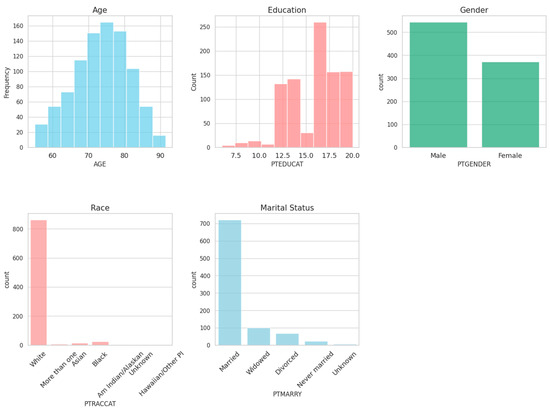
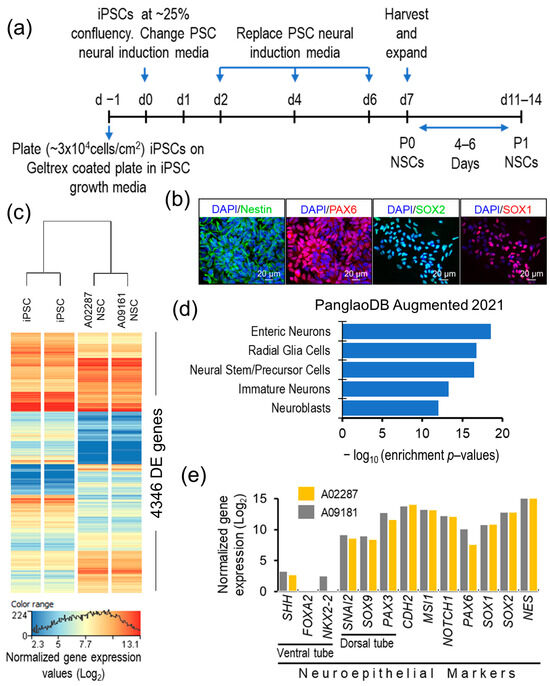
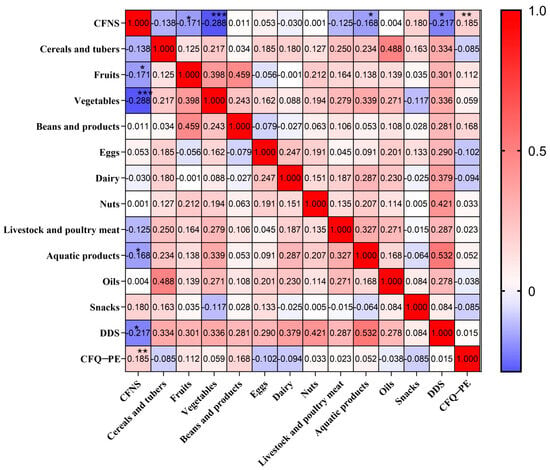
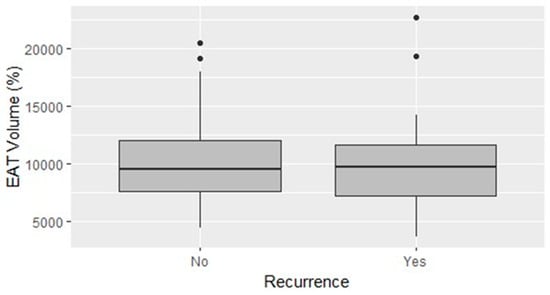
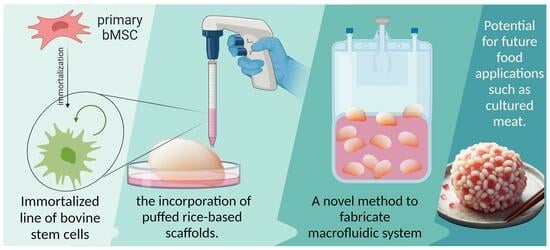
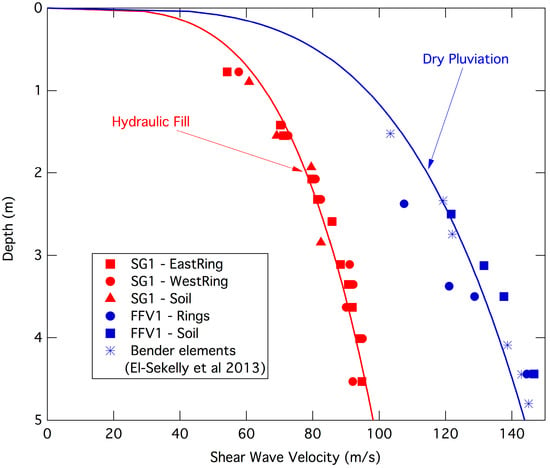
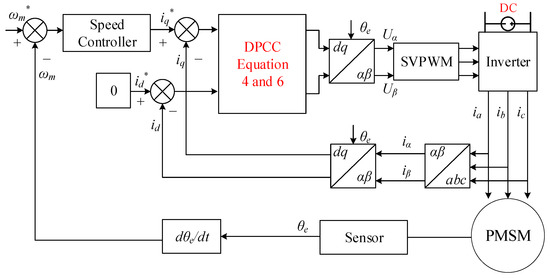
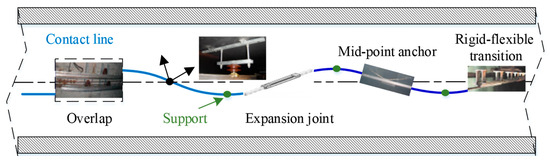
The spatiotemporal expression patterns of genes are crucial for maintaining normal physiological functions in animals. Conditional gene knockout using the cyclization recombination enzyme (
Cre)/locus of crossover of P1 (
Cre/
LoxP) strategy has been extensively employed for functional assays
[...] Read more.
The spatiotemporal expression patterns of genes are crucial for maintaining normal physiological functions in animals. Conditional gene knockout using the cyclization recombination enzyme (
Cre)/locus of crossover of P1 (
Cre/
LoxP) strategy has been extensively employed for functional assays at specific tissue or developmental stages. This approach aids in uncovering the associations between phenotypes and gene regulation while minimizing interference among distinct tissues. Various
Cre-engineered mouse models have been utilized in the male reproductive system, including
Dppa3-
MERCre for primordial germ cells,
Ddx4-
Cre and
Stra8-
Cre for spermatogonia,
Prm1-
Cre and
Acrv1-
iCre for haploid spermatids,
Cyp17a1-
iCre for the Leydig cell,
Sox9-
Cre for the Sertoli cell, and
Lcn5/8/9-
Cre for differentiated segments of the epididymis. Notably, the specificity and functioning stage of
Cre recombinases vary, and the efficiency of recombination driven by
Cre depends on endogenous promoters with different sequences as well as the constructed
Cre vectors, even when controlled by an identical promoter.
Cre mouse models generated via traditional recombination or CRISPR/Cas9 also exhibit distinct knockout properties. This review focuses on
Cre-engineered mouse models applied to the male reproductive system, including
Cre-targeting strategies, mouse model screening, and practical challenges encountered, particularly with novel mouse strains over the past decade. It aims to provide valuable references for studies conducted on the male reproductive system.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT