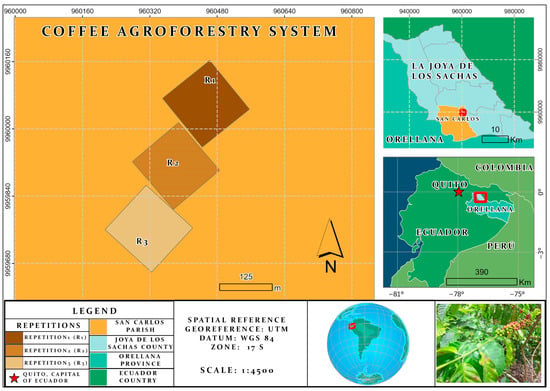
The tumor microenvironment is affected by reactive oxygen species and has been suggested to have an important role in ovarian cancer (OC) tumorigenesis. The role of glutathione transferases (GSTs) in the maintenance of redox balance is considered as an important contributing factor in cancer, including OC. Furthermore, GSTs are mostly encoded by highly polymorphic genes, which further highlights their potential role in OC, known to originate from accumulated genetic changes. Since the potential relevance of genetic variations in omega-class GSTs (
GSTO1 and
GSTO2), with somewhat different activities such as thioltransferase and dehydroascorbate reductase activity, has not been clarified as yet in terms of susceptibility to OC, we aimed to investigate whether the presence of different
GSTO1 and
GSTO2 genetic variants, individually or combined, might represent determinants of risk for OC development. Genotyping was performed in 110 OC patients and 129 matched controls using a PCR-based assay for genotyping single nucleotide polymorphisms. The results of our study show that homozygous carriers of the
GSTO2 variant
G allele are at an increased risk of OC development in comparison to the carriers of the referent genotype (OR1 = 2.16, 95% CI: 0.88–5.26,
p = 0.08; OR2 = 2.49, 95% CI: 0.93–6.61,
p = 0.06). Furthermore, individuals with
GST omega haplotype H2, meaning the concomitant presence of the
GSTO1*A and
GSTO2*G alleles, are more susceptible to OC development, while carriers of the H4
(*A*A) haplotype exhibited lower risk of OC when crude and adjusted haplotype analysis was performed (OR1 = 0.29; 95% CI: 0.12–0.70;
p = 0.007 and OR2 = 0.27; 95% CI: 0.11–0.67;
p = 0.0054). Overall, our results suggest that
GSTO locus variants may confer OC risk.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT