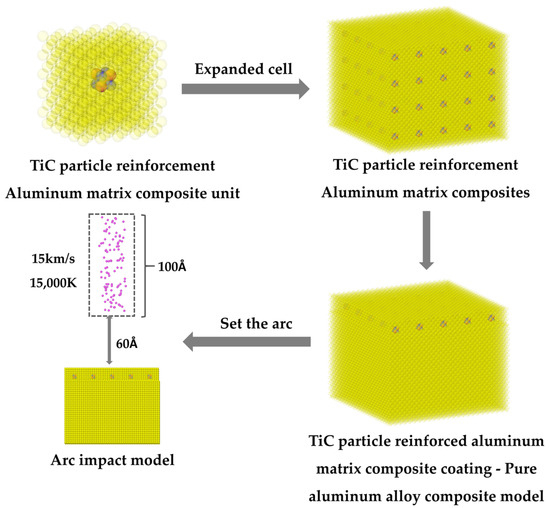
Demethylation inhibitors (DMIs), including prochloraz, are popular fungicides to control citrus postharvest pathogens such as
Penicillium digitatum (green mold). However, many
P. digitatum strains have developed prochloraz resistance, which decreases drug efficacy. Specific major facilitator superfamily (MFS) transporter gene
mfs2, encoding drug-efflux
[...] Read more.
Demethylation inhibitors (DMIs), including prochloraz, are popular fungicides to control citrus postharvest pathogens such as
Penicillium digitatum (green mold). However, many
P. digitatum strains have developed prochloraz resistance, which decreases drug efficacy. Specific major facilitator superfamily (MFS) transporter gene
mfs2, encoding drug-efflux pump protein MFS2, has been identified in
P. digitatum strain F6 (PdF6) to confer fungal strain prochloraz resistance. However, except for the drug-efflux pump function of MFS2, other mechanisms relating to the Pd
mfs2 are not fully clear. The present study reported a transcriptome investigation on the
mfs2-defective
P. digitatum strain. Comparing to the wild-type strain, the
mfs2-defective strain showed 717 differentially expressed genes (DEGs) without prochloraz induction, and 1221 DEGs with prochloraz induction. The obtained DEGs included multiple isoforms of MFS transporter-encoding genes, ATP-binding cassette (ABC) transporter-encoding genes, and multidrug and toxic compound extrusion (MATE) family protein-encoding genes. Many of these putative drug-efflux pump protein-encoding genes had significantly lower transcript abundances in the
mfs2-defective
P. digitatum strain at prochloraz induction, as compared to the wild-type strain, including twenty-two MFS transporter-encoding genes (
MFS1 to
MFS22), two ABC transporter-encoding genes (
ABC1 and
ABC2), and three MATE protein-encoding genes (
MATE1 to
MATE3). The prochloraz induction on special drug-efflux pump protein genes in the wild-type strain was not observed in the
mfs2-defective strain, including
MFS21,
MFS22,
ABC2,
MATE1,
MATE2, and
MATE3. On the other hand, the up-regulation of other drug-efflux pump protein genes in the
mfs2-defective strain cannot recover the fungal prochloraz resistance, including
MFS23,
MFS26,
MFS27,
MFS31,
MFS33, and
ABC3 to
ABC8. The functional enrichment of DEGs based on Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG), Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG), and euKaryotic Orthologous Groups (KOG) database resources suggested some essential contributors to the
mfs2-relating prochloraz resistance, including ribosome biosynthesis-related genes, oxidative phosphorylation genes, steroid biosynthesis-related genes, fatty acid and lipid metabolism-related genes, and carbon- and nitrogen-metabolism-related genes. The results indicated that the MFS2 transporter might be involved in the regulation of multiple drug-efflux pump protein gene expressions and multiple metabolism-related gene expressions, thus playing an important role in developing
P. digitatum prochloraz resistance.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT