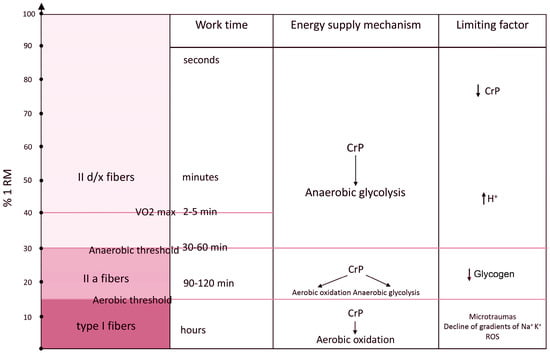
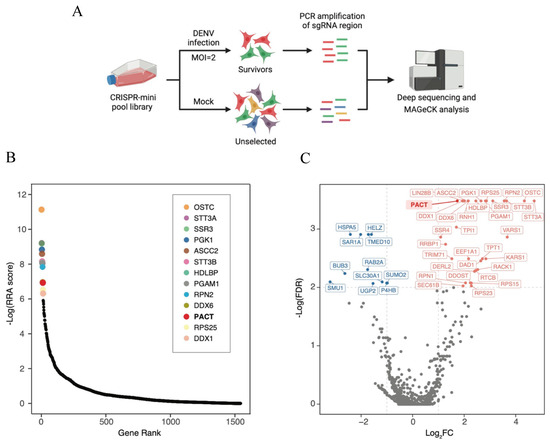
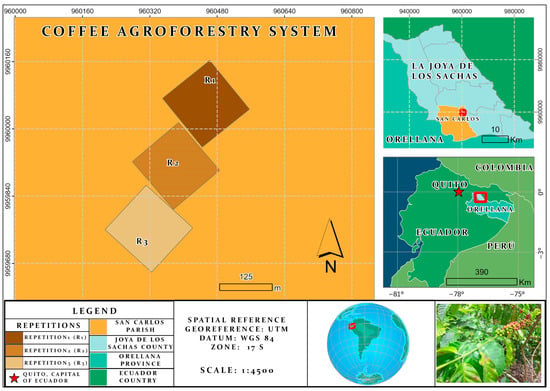
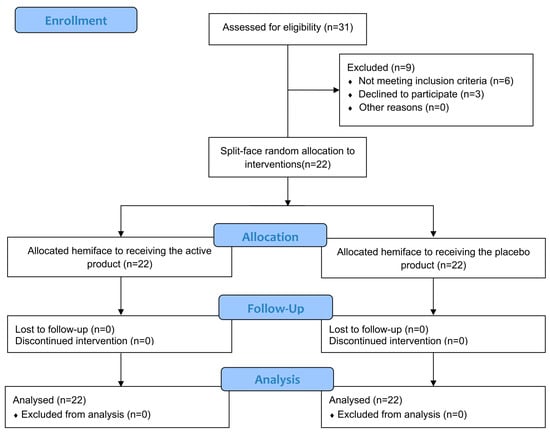
Background: Steatotic liver disease (SLD) has been linked to more exacerbated inflammatory responses in various scenarios. The relationship between SLD and COVID-19 prognosis remains unclear. Our aim was to investigate the impact of SLD on the outcome of COVID-19.
Methods: Patients hospitalized with confirmed COVID-19 and who underwent laboratory tests and chest CT scans were included. SLD was assessed by measuring the attenuation coefficient on CT scans. The relationship between SLD, the severity of COVID-19 clinical presentation and in-hospital mortality were assessed.
Results: A total of 610 patients were included (mean age 62 ± 16 years, 64% male). The prevalence of SLD was 30%, and the overall in-hospital mortality rate was 19%. Patients with SLD were younger (58 ± 13 vs. 64 ± 16 years,
p < 0.001) and had a higher BMI (32 ± 5 vs. 28 ± 4 kg/m
2,
p = 0.014). Admission AST values were higher in patients with SLD (82 ± 339 vs. 50 ± 37,
p = 0.02), while D-dimer (1112 ± 2147 vs. 1959 ± 8509,
p = 0.07), C-reactive protein (12 ± 9 vs. 11 ± 8,
p = 0.27), ALT (67 ± 163 vs. 47 ± 90,
p = 0.11), ALP (83 ± 52 vs. 102 ± 125,
p = 0.27), and GGT (123 ± 125 vs. 104 ± 146,
p = 0.61) did not significantly differ compared to patients without SLD. No difference was observed regarding lung parenchyma involvement >50% (20% vs. 17%,
p = 0.25), hospital length of stay (14 ± 19 vs. 16 ± 23 days,
p = 0.20), hemodialysis support (14% vs. 16%,
p = 0.57), use of mechanical ventilation (20% vs. 20%,
p = 0.96), and in-hospital mortality (17% vs. 20%,
p = 0.40) when comparing patients with and without SLD.
Conclusions: SLD showed no significant association with morbidity and mortality in patients with COVID-19.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT