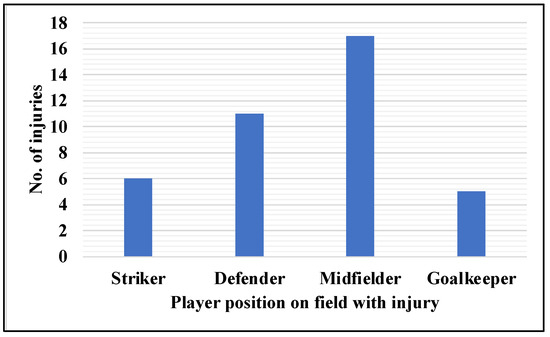
Ralstonia eutropha strain H16 is a chemoautotrophic bacterium that oxidizes hydrogen and accumulates poly[(
R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] [P(3HB)], a prominent polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), within its cell.
R. eutropha utilizes fructose or CO
2 as its sole carbon source for this process. A PHA-negative mutant of
[...] Read more.
Ralstonia eutropha strain H16 is a chemoautotrophic bacterium that oxidizes hydrogen and accumulates poly[(
R)-3-hydroxybutyrate] [P(3HB)], a prominent polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA), within its cell.
R. eutropha utilizes fructose or CO
2 as its sole carbon source for this process. A PHA-negative mutant of strain H16, known as
R. eutropha strain PHB
−4, cannot produce PHA. Strain 1F2, derived from strain PHB
−4, is a leucine analog-resistant mutant. Remarkably, the recombinant 1F2 strain exhibits the capacity to synthesize 3HB-based PHA copolymers containing 3-hydroxyvalerate (3HV) and 3-hydroxy-4-methyvalerate (3H4MV) comonomer units from fructose or CO
2. This ability is conferred by the expression of a broad substrate-specific PHA synthase and tolerance to feedback inhibition of branched amino acids. However, the total amount of comonomer units incorporated into PHA was up to around 5 mol%. In this study, strain 1F2 underwent genetic engineering to augment the comonomer supply incorporated into PHA. This enhancement involved several modifications, including the additional expression of the broad substrate-specific 3-ketothiolase gene (
bktB), the heterologous expression of the 2-ketoacid decarboxylase gene (
kivd), and the phenylacetaldehyde dehydrogenase gene (
padA). Furthermore, the genome of strain 1F2 was altered through the deletion of the 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase gene (
hbdH). The introduction of
bktB-kivd-padA resulted in increased 3HV incorporation, reaching 13.9 mol% from fructose and 6.4 mol% from CO
2. Additionally, the
hbdH deletion resulted in the production of PHA copolymers containing (
S)-3-hydroxy-2-methylpropionate (3H2MP). Interestingly,
hbdH deletion increased the weight-average molecular weight of the PHA to over 3.0 × 10
6 on fructose. Thus, it demonstrates the positive effects of
hbdH deletion on the copolymer composition and molecular weight of PHA.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT