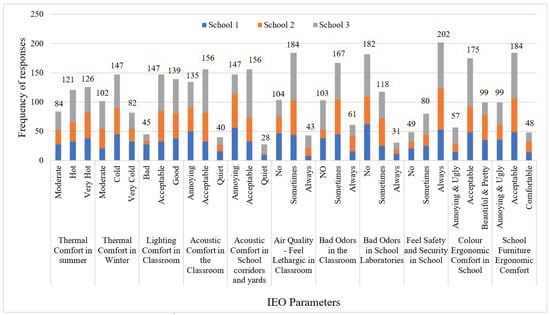
The aim of this study was to explore the characteristics of the combined application of organic fertilizer and inorganic fertilizer using different tillage methods to delay the senescence of maize leaves. The yield and activities of GDH, CAT, APX, GR, and GSH enzymes
[...] Read more.
The aim of this study was to explore the characteristics of the combined application of organic fertilizer and inorganic fertilizer using different tillage methods to delay the senescence of maize leaves. The yield and activities of GDH, CAT, APX, GR, and GSH enzymes in maize leaves were measured at different growth stages by using two tillage methods, three organic and inorganic combined applications (P
1, P
2, and P
3), and four control treatments. (1) During the growth period, the R + S and R treatments were P
1 treatments, with the highest enzyme activities noted for GDH, CAT, APX, GR, and GSH, which were 36.79–103.22% higher than those of CK. (2) The average yield of all R + S treatments was higher than that of R treatments, and the average yield of P1 treatment was the highest under R + S, which was 13,663.79 kg hm
−2, which was 6.39%, 7.90%, and 14.67% higher than that of P
2, P
3, and CK, respectively, which was lower than that of R. The yield of P
1 treatment was 2.53% higher. (3) There was a significant positive correlation between APX activity, CAT activity, GR activity, GDH activity, GSH activity, grain number per ear, ear length, and 100-grain weight of maize leaves at the grain filling stage, and a significant negative correlation between bald tip length and yield. The treatment details had the strongest enzyme activity and the highest yield when using the rotary tillage + subsoiling (R + S) P
1 method, which was the most suitable tillage method and the best fertilizer ratio combination, which could be demonstrated and popularized in a large area in the dry farming area of spring maize in Shanxi Province.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT