Objectives: Addressing extensive and deep burn wounds poses considerable challenges for both patients and surgeons. The NovoSorb
® Biodegradable Temporizing Matrix (BTM) emerged as a novel dermal substitute and has been subjected to evaluation in large burn wound cases, with a specific focus on identifying risk factors associated with suboptimal take rates.
Methods: All patients with burn wounds greater than 10% body surface that underwent BTM treatment between March 2020 and November 2023 were eligible for inclusion. Univariate analyses and linear regression models were employed to discern risk factors and predictors influencing the take rates of both the BTM and split-thickness skin grafts (STSGs).
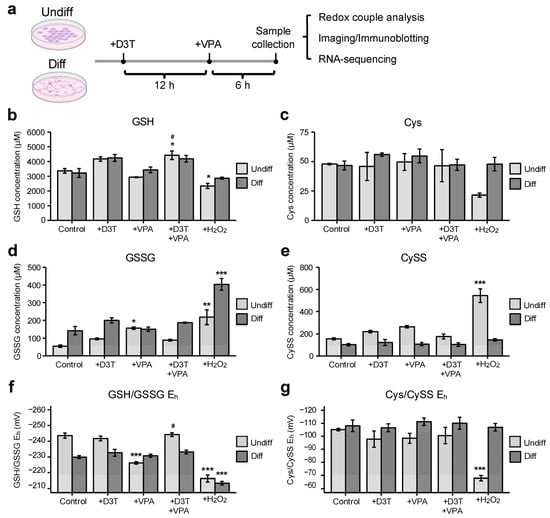
Results: A total of 175 patients (mean age 56.2 ± 19.8 years, 70.3% male) were evaluated. The mean take rates of the BTM and STSGs were 82.0 ± 24.7% and 87.3 ± 19.0%, respectively. There were significant negative correlations between BTM take and the number of surgeries before BTM application (r = −0.19,
p = 0.01), %TBSA and STSG take (r = −0.36,
p = <0.001) and significant positive correlations between BTM and STSG take (r = 0.41,
p ≤ 0.001) in addition to NPWT and STSG take (r = 0.21,
p = 0.01). Multivariate regression analyses showed that a larger number of surgeries prior to BTM application (OR −3.41, 95% CI −6.82, −0.03,
p = 0.04) was associated with poorer BTM take. Allograft treatment before BTM application (OR −14.7, 95% CI −23.0, −6.43,
p = 0.01) and failed treatment with STSG before BTM application (OR −20.8, 95% CI −36.3, −5.23,
p ≤ 0.01) were associated with poorer STSG take, whereas higher BTM take rates were associated with overall higher STSG take (OR −0.15, 95% 0.05, 0.26,
p = 0.01). The Meek technique was used in 24 patients and showed similar take rates (BTM: 76.3 ± 28.0%,
p = 0.22; STSG: 80.7 ± 21.1,
p = 0.07).
Conclusions: This study summarizes our findings on the application of a BTM in the context of large burn wounds. The results demonstrate that successful treatment can be achieved even in patients with extensive burns, resulting in satisfying take rates for both the BTM and STSG. The data underscore the importance of promptly applying a BTM to debrided wounds and indicate good results when using Meek.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT