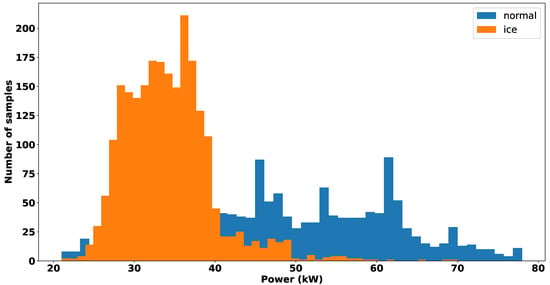
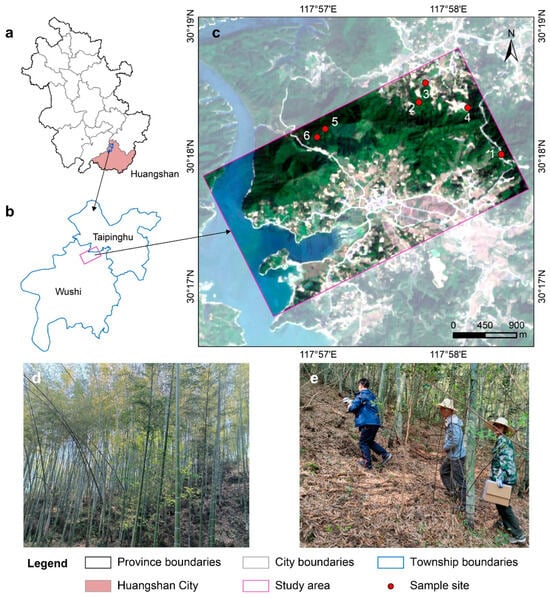
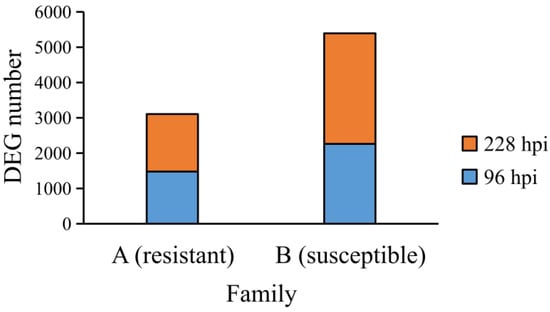
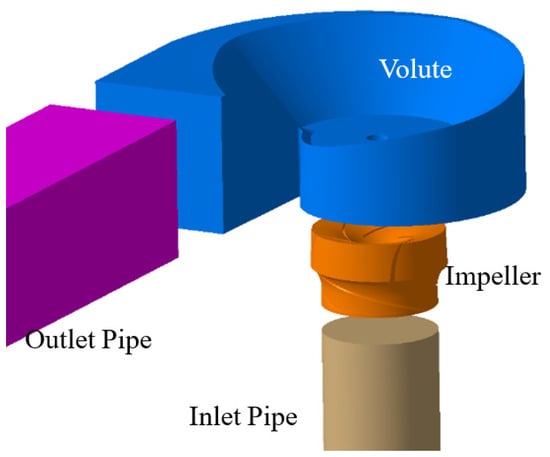
In this research, we elucidated the species composition of
Culicoides biting midges, infection prevalence, and genetic diversity of
Leishmania parasites circulating in the affected community in Chiang Rai Province, being the most endemic area in Northern Thailand. A total of 146 parous and
[...] Read more.
In this research, we elucidated the species composition of
Culicoides biting midges, infection prevalence, and genetic diversity of
Leishmania parasites circulating in the affected community in Chiang Rai Province, being the most endemic area in Northern Thailand. A total of 146 parous and gravid females, belonging to at least twelve
Culicoides species in five subgenera and one species group, were trapped from three collection sites with an overall
Leishmania prevalence of 26.7% (39/146).
Leishmania was detected, using
ITS1-PCR, in
C. mahasarakamense (15),
C. guttifer (11),
C. (
Trithecoides) spp. (8),
C. jacobsoni (2),
C. oxystoma (2), and
C. orientalis (1). The evidence of
Leishmania infection in these last five species represents new records in Northern Thailand. Given a high infection rate in cavernicolous specimens, this indicates an increased risk of parasite exposure when visiting the cave. Using the nanopore amplicon sequencing,
L. martiniquensis was ubiquitously identified in all positives, and more than half of these were also co-infected with
L. orientalis. The genetic diversity analysis revealed 13 and 17 unique haplotypes for
L. martiniquensis and
L. orientalis, respectively. Higher haplotype diversity and relatively low nucleotide diversity were observed in both parasite populations, suggesting recent population divergence. Neutrality tests (Tajima’s
D and Fu and Li’s
D) showed to be significantly negative, indicating rapid population growth or a selective sweep. Moreover, dominant haplotypes of both
Leishmania species were 100% identical to those in all leishmaniasis patients previously reported from Northern Thailand, strongly supporting the imperative role of
Culicoides spp. in disease transmission. Essentially, this research provides the first entomological surveillance data representing the sympatric existence, transmission dynamics, and genetic complexity of two autochthonous
Leishmania (
Mundinia) parasites in several
Culicoides species in the endemic area of Northern Thailand. This would contribute to a more complete understanding of the epidemiology of vector infection and facilitate the development of vector control programs to effectively reduce the transmission of this neglected tropical disease in endemic areas of Northern Thailand.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT