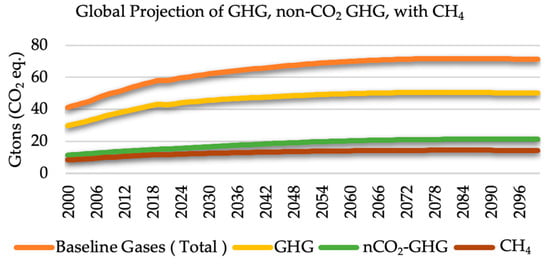
The role of methane (CH
4) in the 21st century presents a critical dilemma. Its abundance and clean-burning nature make it a promising energy source, while its potent greenhouse effect threatens climate stability. Despite its potent greenhouse gas (GHG) nature, CH
4 remains a crucial energy resource. However, advancements in CH
4 capture, utilization, and emissions mitigation are rapidly evolving, necessitating a critical assessment of the advances, their potential, and challenges. This study aims to comprehensively evaluate the current state of the art in these advancements, particularly focusing on the emissions trends, with corresponding global warming potentials of projected CH
4 emissions, and a discussion on the advances that have been made towards reducing the impacts of CH
4 emissions. The areas of these advances include measurement, computational, numerical modeling, and simulation studies for CH
4, emerging technologies for CH
4 production, management and control, the nexus of CH
4 –X, and case study applications in countries. This study reports on these advances, which involves a technical review of studies, mainly from the last decade, discussing the technical feasibility, economic viability, and environmental impact of these advancements. Our trend analysis reveals that even though the share of CH
4 in the GHG mix has been around 19% compared with carbon dioxide (CO
2), still, CH
4 reduction would need to be highly subsidized because of the high global warming potential it has, compared with CO
2. We conclude that while significant progress has been made, further research and development are essential to optimize the performance, scalability, and affordability of these advancements. Additionally, robust policy frameworks and international collaborations are crucial to ensure widespread adoption and maximize the potential that comes with the advancements in the mitigation of the impact of CH
4 emission. This study contributes to the ongoing dialogue on balancing the potentials of CH
4 with its environmental footprint, paving the way for a future where this versatile resource can be utilized sustainably.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT