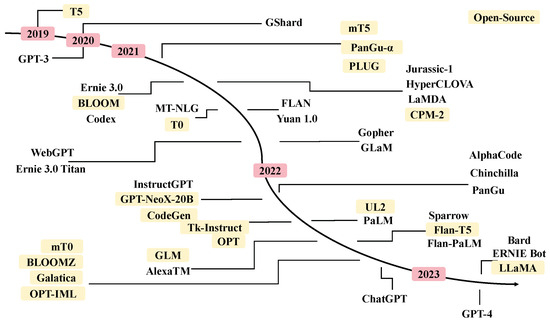
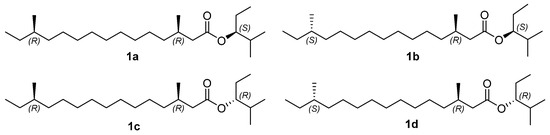
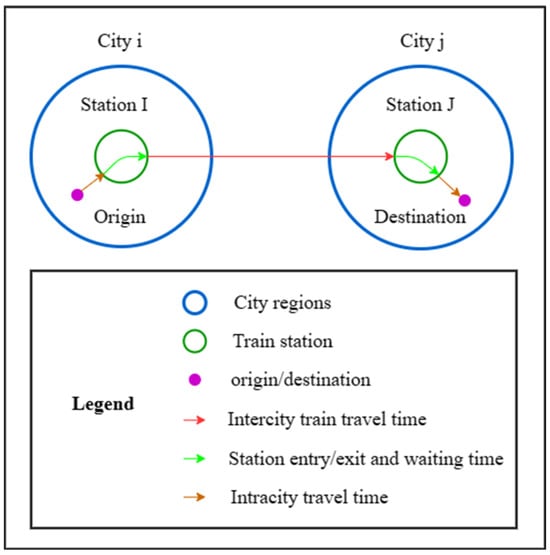
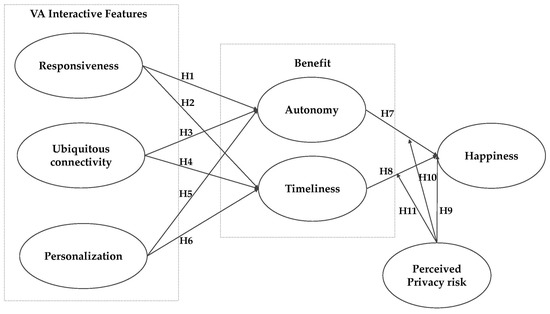
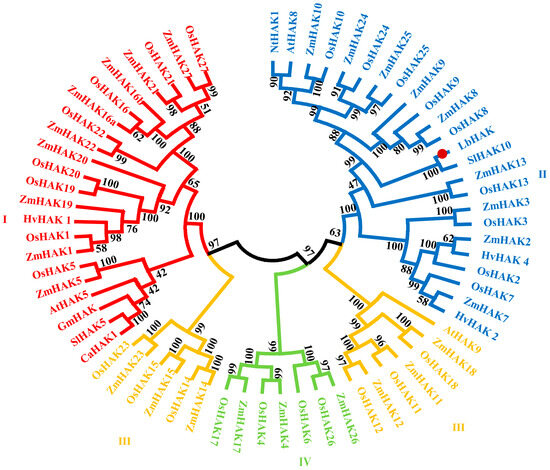
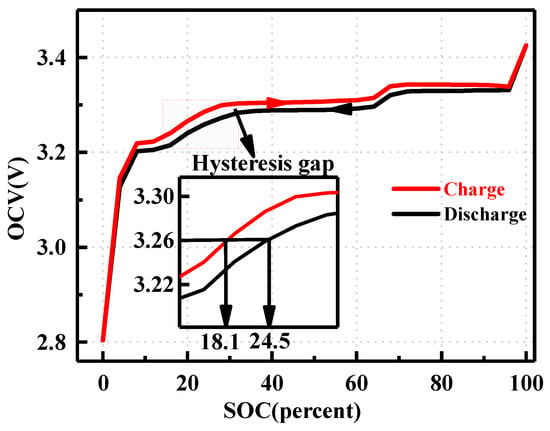
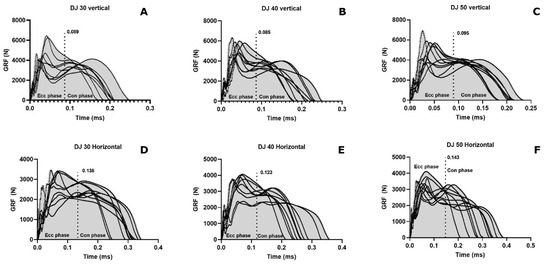
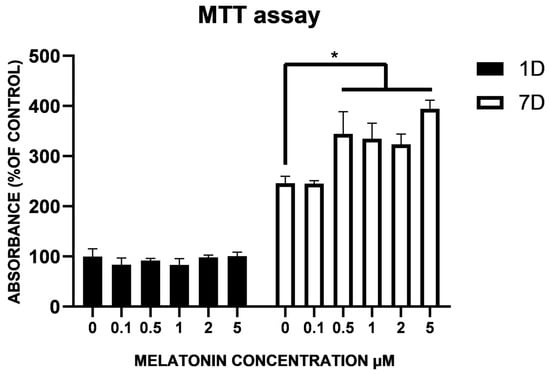
Due to a higher risk of maternal complications during pregnancy, as well as pregnancy complications such as stillbirth, SARS-CoV-2 contamination during pregnancy is a putative stress factor that could increase the risk of perinatal maternal mental health issues. We included women older than 18 years, who delivered a living baby at the Geneva University Hospitals’ maternity wards after 29 weeks of amenorrhea (w.a.) and excluded women who did not read or speak fluent French. We compared women who declared having had COVID-19, confirmed by a positive PCR test for SARS-CoV-2, during pregnancy with women who did not, both at delivery and at one month postpartum. We collected clinical data by auto-questionnaires between time of childbirth and the third day postpartum regarding the occurrence of perinatal depression, peritraumatic dissociation, and peritraumatic distress during childbirth, measured, respectively, by the EPDS (depression is score > 11), PDI (peritraumatic distress is score > 15), and PDEQ (scales). At one month postpartum, we compared the proportion of women with a diagnosis of postpartum depression (PPD) and birth-related posttraumatic stress disorder (CB-PTSD), using PCL-5 for CB-PTSD and using diagnosis criteria according DSM-5 for both PPD and CB-PTSD, in the context of a semi-structured interview, conducted by a clinician psychologist. Off the 257 women included, who delivered at the University Hospitals of Geneva between 25 January 2021 and 10 March 2022, 41 (16.1%) declared they had a positive PCR test for SARS-CoV-2 during their pregnancy. Regarding mental outcomes, except birth-related PTSD, all scores provided higher mean values in the group of women who declared having been infected by SARS-CoV-2, at delivery and at one month postpartum, without reaching any statistical significance: respectively, 7.8 (±5.2, 8:4–10.5) versus 6.5 (±4.7, 6:3–9),
p = 0.139 ***, for continuous EPDS scores; 10 (25.0) versus 45 (21.1),
p = 0.586 *, for dichotomous EPDS scores (≥11); 118 (55.7) versus 26 (63.4),
p = 0.359 *, for continuous PDI scores; 18.3 (±6.8, 16:14–21) versus 21.1 (±10.7, 17:15–22), 0.231 ***, for dichotomous PDI scores (≥15); 14.7 (±5.9, 13:10–16) versus 15.7 (±7.1, 14:10–18),
p = 0.636 ***, for continuous PDEQ scores; 64 (30.0) versus 17 (41.5),
p = 0.151 *, for dichotomous PDEQ scores (≥15); and 2 (8.0) versus 5 (3.6),
p = 0.289 *, for postpartum depression diagnosis, according DSM-5. We performed Chi-squared or Fisher’s exact tests, depending on applicability for the comparison of categorical variables and Mann–Whitney nonparametric tests for continuous variables;
p < 0.05 was considered as statistically significant. Surprisingly, we did not find more birth-related PTSD as noted by the PCL-5 score at one month postpartum in women who declared a positive PCR test for SARS-CoV-2:15 (10.6) versus no case of birth related PTSD in women who were infected during pregnancy (
p = 0.131 *). Our study showed that mental outcomes were differently distributed between women who declared having been infected by SARS-CoV-2 compared to women who were not infected. However, our study was underpowered to explore all the factors associated with psychiatric issues during pregnancy, postpartum, depending on the exposure to SARS-CoV-2 infection during pregnancy. Future longitudinal studies on bigger samples and more diverse populations over a longer period are needed to explore the long-term psychic impact on women who had COVID-19 during pregnancy.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT