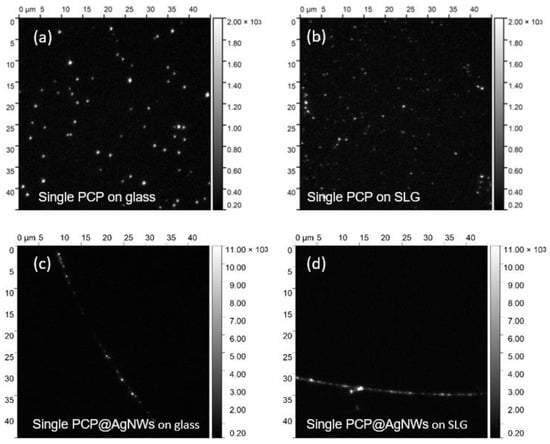
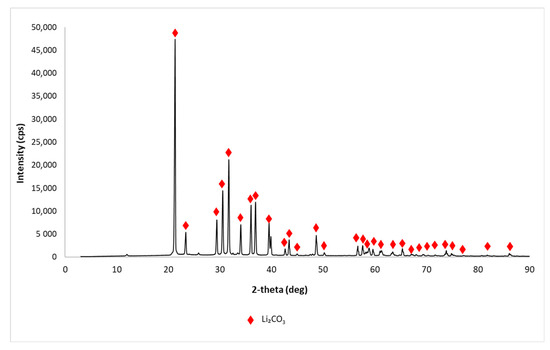
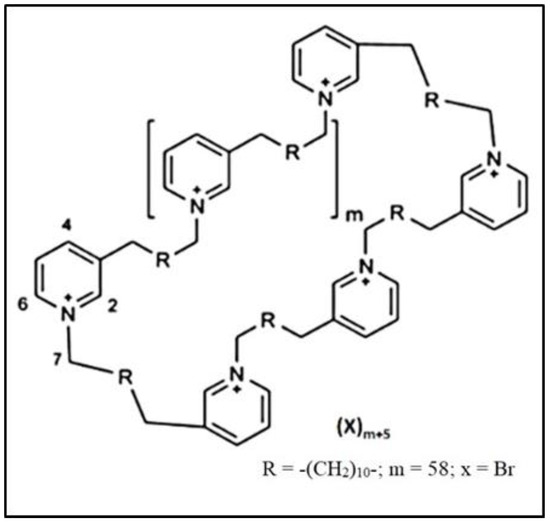
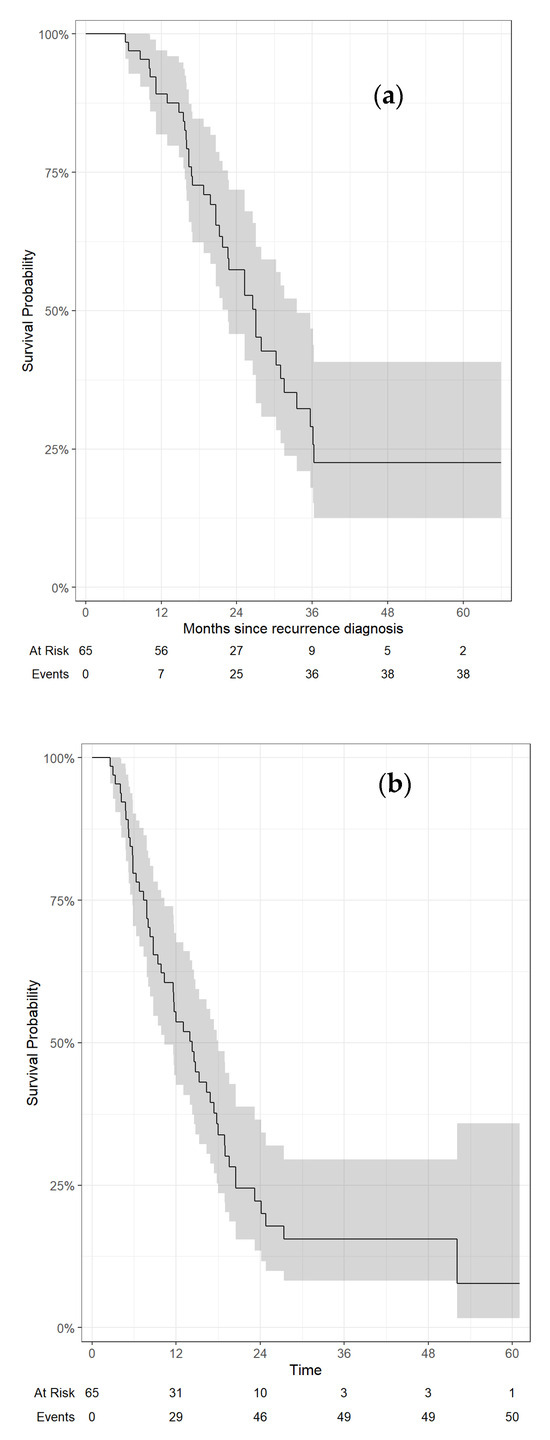
Background: A previous report showed that the urine output of HPLBII-P in patients with diabetes mellitus and SARS-CoV-2 infection was increased as a sign of glomerular dysfunction. The aim of this report was to investigate the relation of the urine output of HPLBII-P to diabetes mellitus in two large community-based elderly populations, i.e., the ULSAM and PIVUS cohorts.
Methods: HPLBII-P was measured by an ELISA in the urine of a community-based cohort of 839 men (ULSAM) collected at 77 years of age and in the urine of a community-based cohort of 75-year-old men, n = 387, and women, n = 401 (PIVUS). KIM-1, NGAL, and albumin were measured in urine and cathepsin S and cystatin C in serum.
Results: HPLBII-P was significantly raised among males with diabetes in the ULSAM (
p < 0.0001) and PIVUS cohorts (
p ≤ 0.02), but not in the female cohort of PIVUS. In the female subpopulation of insulin-treated diabetes, HPLBII-P was raised (
p = 0.02) as compared to women treated with oral antidiabetics only. In the ULSAM cohort, HPLBII-P was correlated to NGAL, KIM-1, and albumin in urine both in non-DM (all three biomarkers;
p < 0.0001) and in DM (NGAL;
p = 0.002, KIM-1;
p = 0.02 and albumin;
p = 0.01). Plasma glucose and HbA1c in blood showed correlations to U-HPLBII-P (r = 0.58,
p < 0.001 and r = 0.42,
p = 0.004, respectively). U-HPLBII-P and cathepsin S were correlated in the ULSAM group (r = 0.50,
p < 0.001). No correlations were observed between U-HPLBII-P and serum creatinine or cystatin C.
Conclusions: The urine measurement of HPLBII-P has the potential to become a novel and useful biomarker in the monitoring of glomerular activity in diabetes mellitus.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT