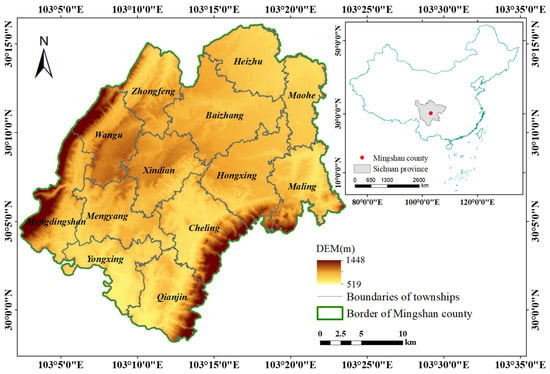
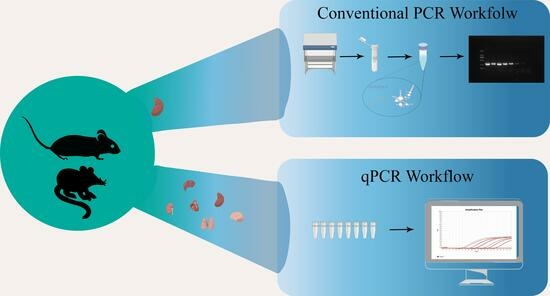
Bartonella is an intracellular parasitic zoonotic pathogen that can infect animals and cause a variety of human diseases. This study investigates
Bartonella infection in small mammals in Yunnan Province, China, focusing on tissue tropism. A total of 333 small mammals were sampled from
[...] Read more.
Bartonella is an intracellular parasitic zoonotic pathogen that can infect animals and cause a variety of human diseases. This study investigates
Bartonella infection in small mammals in Yunnan Province, China, focusing on tissue tropism. A total of 333 small mammals were sampled from thirteen species, three orders, four families, and four genera in Heqing and Gongshan Counties. Conventional PCR and real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) were utilized for detection and quantification, followed by bioinformatic analysis of obtained DNA sequences. Results show a 31.5% detection rate, varying across species. Notably,
Apodemus chevrieri, Eothenomys eleusis, Niviventer fulvescens, Rattus tanezumi, Episoriculus leucops, Anourosorex squamipes, and
Ochotona Thibetana exhibited infection rates of 44.4%, 27.7%, 100.0%, 6.3%, 60.0%, 23.5%, and 22.2%, respectively. Genetic analysis identified thirty, ten, and five strains based on
ssrA,
rpoB, and
gltA genes, with nucleotide identities ranging from 92.1% to 100.0%.
Bartonella strains were assigned to
B. grahamii,
B. rochalimae,
B. sendai,
B. koshimizu,
B. phoceensis,
B. taylorii, and a new species identified in
Episoriculus leucops (GS136). Analysis of the different tissues naturally infected by
Bartonella species revealed varied copy numbers across different tissues, with the highest load in spleen tissue. These findings underscore
Bartonella’s diverse species and host range in Yunnan Province, highlighting the presence of extensive tissue tropism in
Bartonella species naturally infecting small mammalian tissues.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT