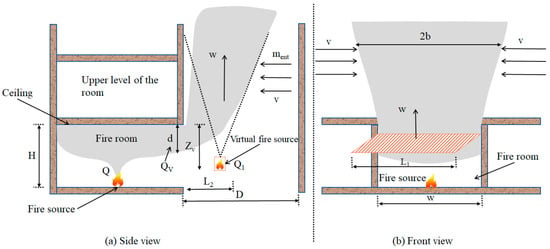
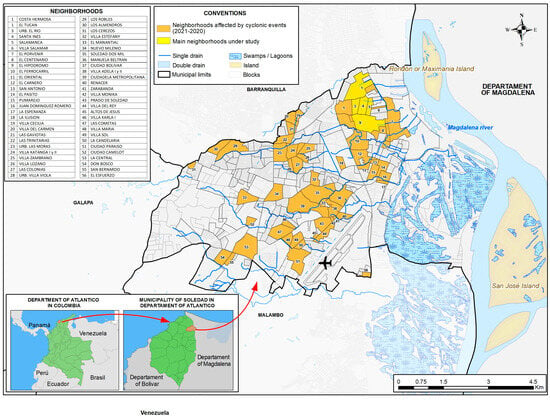
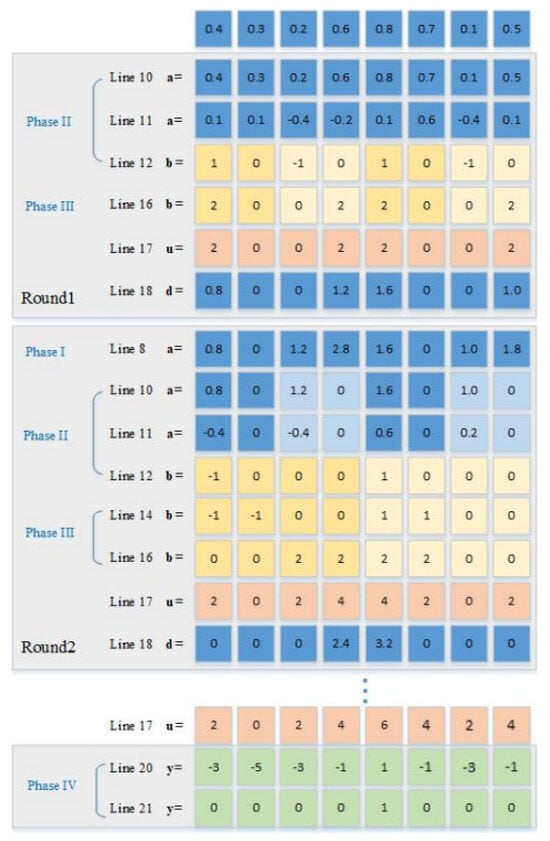
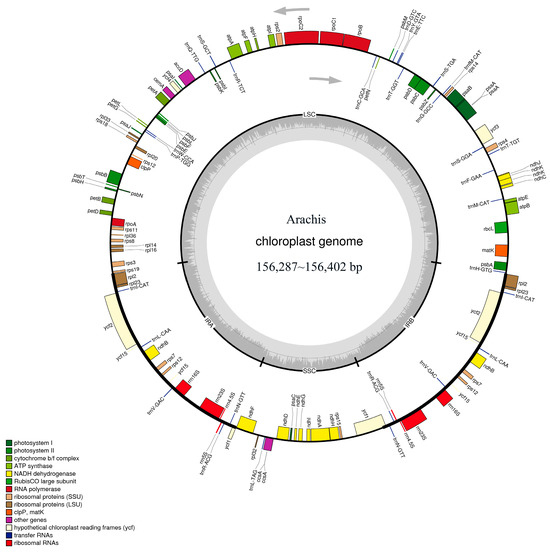
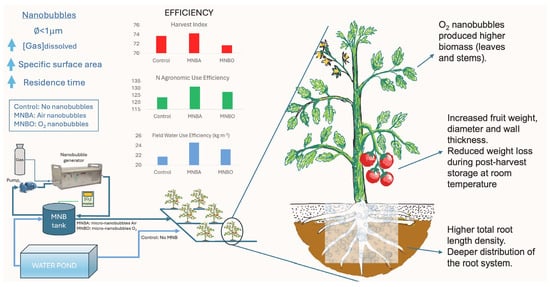
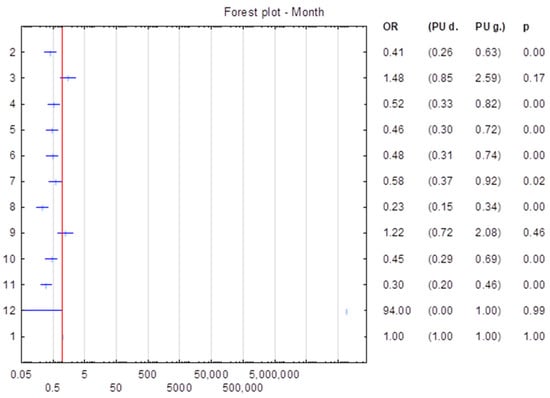
Camellia oleifera is a woody, edible-oil plant native to China. Anthracnose is the major disease of
Ca. oleifera, and
Colletotrichum fructicola is the main epidemic pathogen. Our previous research indicated that CfHac1 (homologous to ATF/CREB1) and CfGcn5 (general control nonderepressible 5, Gcn5)
[...] Read more.
Camellia oleifera is a woody, edible-oil plant native to China. Anthracnose is the major disease of
Ca. oleifera, and
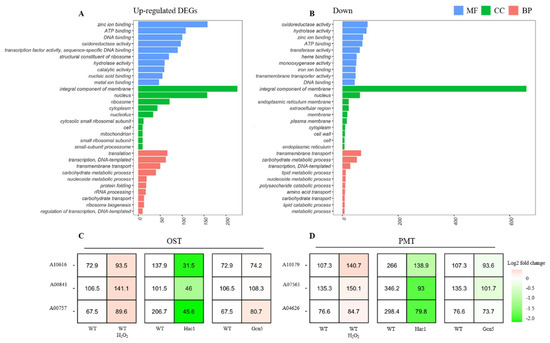
Colletotrichum fructicola is the main epidemic pathogen. Our previous research indicated that CfHac1 (homologous to ATF/CREB1) and CfGcn5 (general control nonderepressible 5, Gcn5) are integral to key cellular processes that govern fungal development and pathogenesis. Further transcriptomic analyses of the CfHac1 and CfGcn5 mutants, particularly under conditions of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, hold the potential to unveil additional genes implicated in this critical cellular response. We identified all
OST/PMT (oligosaccharyltransferase/Protein
O-Mannosyltransferases) genes in
C. fructicola and analyzed their expression levels. To elucidate novel glycosylation-related genes that may be important for the virulence of
C. fructicola, we took an unbiased transcriptomic approach comparing wild-type and the ∆
Cfhac1 mutant. Notably, all
OST/PMT genes were induced by dithiothreitol and down-regulated in the Δ
Cfhac1 mutant, yet only the
CfPMT4 (Protein
O-Mannosyltransferases 4) gene (A04626) was unaffected in the Δ
Cfgcn5. The results of targeted gene deletion experiments indicate that
CfPMT4 plays a crucial role in both vegetative growth and conidiation. Additionally, our investigation revealed that the Δ
Cfpmt4 exhibits deficiencies in appressorium formation, as well as in its response to cell wall integrity and endoplasmic reticulum stresses. Furthermore, the mutant displayed impaired glycogen metabolism, which may contribute to reduced penetration ability. Overall, CfPmt4, an
O-mannosyltransferase, controls the growth, development, and pathogenicity of
Colletotrichum fructicola. Understanding the function of the
CfPMT4 homolog could provide a potential molecular target for controlling
Ca. oleifera anthracnose.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT