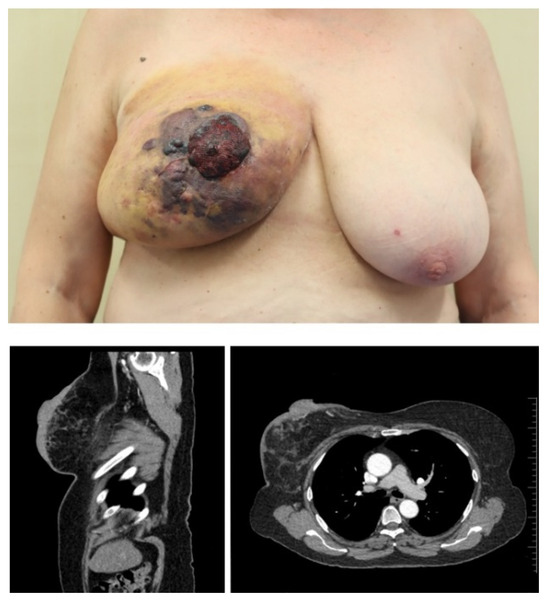
Bivalves hold an important role in marine aquaculture and the identification of growth-related genes in bivalves could contribute to a better understanding of the mechanism governing their growth, which may benefit high-yielding bivalve breeding. Somatostatin receptor (SSTR) is a conserved negative regulator of growth in vertebrates. Although
SSTR genes have been identified in invertebrates, their involvement in growth regulation remains unclear. Here, we identified seven
SSTRs (
PySSTRs) in the Yesso scallop,
Patinopecten yessoensis, which is an economically important bivalve cultured in East Asia. Among the three
PySSTRs (
PySSTR-1,
-2, and
-3) expressed in adult tissues,
PySSTR-1 showed significantly lower expression in fast-growing scallops than in slow-growing scallops. Then, the function of this gene in growth regulation was evaluated in dwarf surf clams (
Mulinia lateralis), a potential model bivalve cultured in the lab, via RNA interference (RNAi) through feeding the clams
Escherichia coli containing plasmids expressing double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) targeting
MlSSTR-1. Suppressing the expression of
MlSSTR-1, the homolog of
PySSTR-1 in
M. lateralis, resulted in a significant increase in shell length, shell width, shell height, soft tissue weight, and muscle weight by 20%, 22%, 20%, 79%, and 92%, respectively. A transcriptome analysis indicated that the up-regulated genes after
MlSSTR-1 expression inhibition were significantly enriched in the fat digestion and absorption pathway and the insulin pathway. In summary, we systemically identified the
SSTR genes in
P. yessoensis and revealed the growth-inhibitory role of
SSTR-1 in bivalves. This study indicates the conserved function of somatostatin signaling in growth regulation, and ingesting dsRNA-expressing bacteria is a useful way to verify gene function in bivalves.
SSTR-1 is a candidate target for gene editing in bivalves to promote growth and could be used in the breeding of fast-growing bivalves.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT