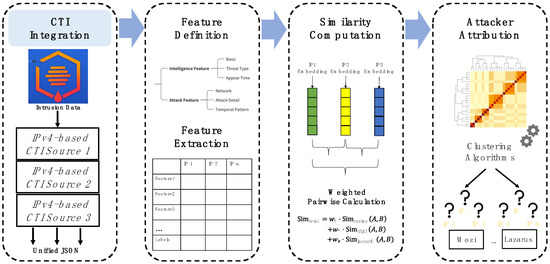
In non-Markovian tandem queueing networks the output process of one site, which is the input process to the next site, is not renewal. Consequently, the correlation analysis of that output processes is essential when studying such networks. A correlation analysis in the M/G/1 queue has been studied in the literature via derivation of the joint Laplace-Stieltjes transform (LST) of the sum of two consecutive inter-departure times. That LST is obtained by considering all possible cases at departure epochs. However, those epochs are expressed via dependent variables. In this paper, we first extend the analysis to the more general
PH/
G/1 queue, and investigate various queues, such as
E2/
G/1 and
C2/
C2/1. Then, we consider the lag-
n correlation, which requires derivation of the joint LST of sum of
n + 1 consecutive inter-departure times. Yet, deriving this LST by the common approach becomes impractical for
n + 1 ≥ 3, as the number of all possible cases at departure epochs increases significantly. To overcome this obstacle, we derive a corresponding single-parameter LST, which expresses the sum of
n+1 consecutive inter-departure times via the (
n + 1)-st departure epoch only. Consequently, the latter LST is expressed via a much fewer number of possible cases, and not less important, as a function of independent variables only, eliminating the need to derive the corresponding joint density. Considering the
M/
G/1 and the
E2/
G/1 queues, we demonstrate that the joint LST can be reconstructed directly via the corresponding single-parameter LST when
n + 1 = 2. We further conjecture that the multi-parameter joint LST can be reconstructed from the corresponding single-parameter LST in more general queues and for values of
n + 1 > 2. The conjecture is validated for various
PH/
G/1 queues and proved for
n + 1 = 3 in the
M/
G/1 case. The new approach facilitates the calculation of lag-
n correlation of the departure process from
PH/
G/1 queue for
n + 1 ≥ 3. Our analysis illuminates the cases when using renewal approximation of the output process provides a proper approximation when studying non-Markovian stochastic networks.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT