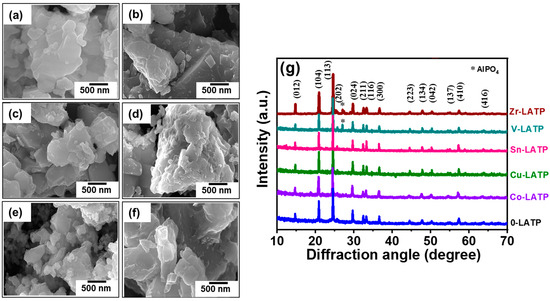
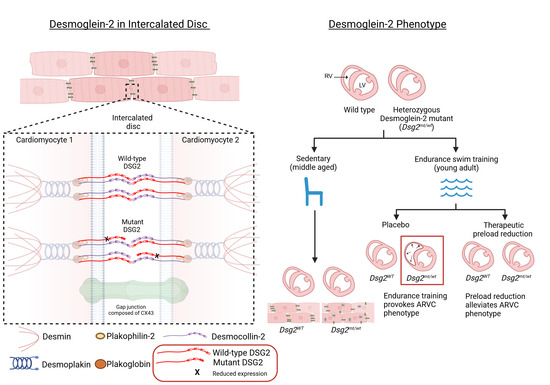
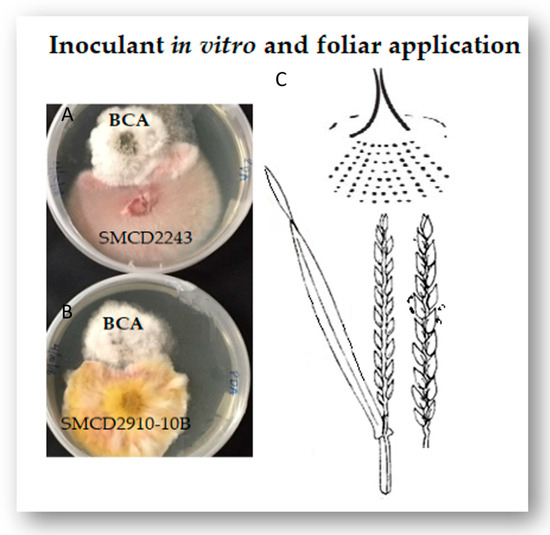
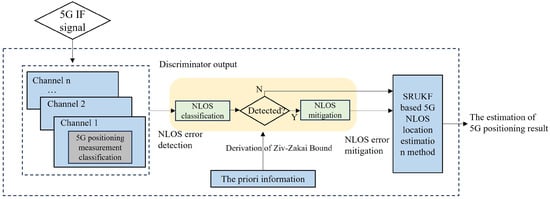
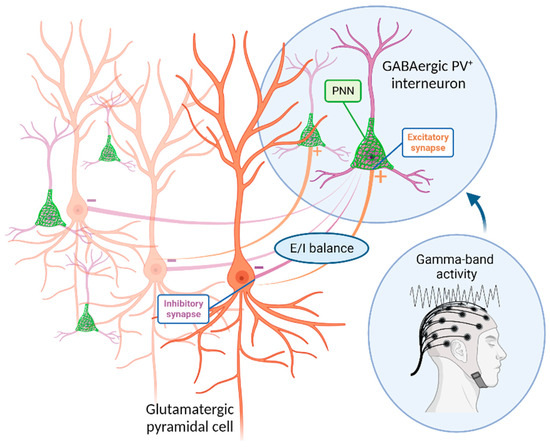
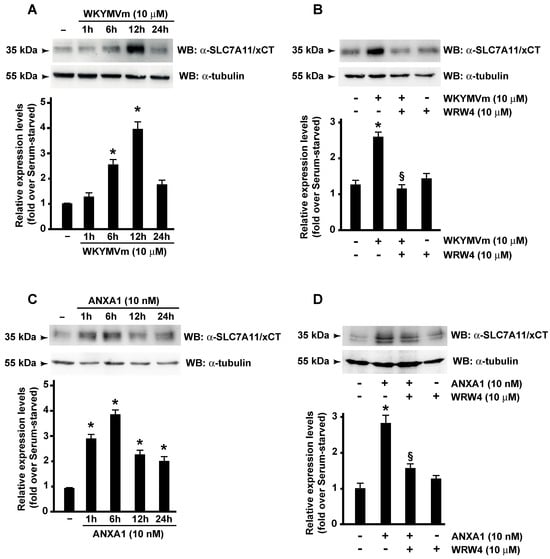
Bitterness from phenylthiocarbamide and 6-n-propylthiouracil (PROP) varies with polymorphisms in the
TAS2R38 gene. Three SNPs form two common (AVI, PAV) and four rare haplotypes (AAI, AAV, PVI, and PAI). AVI homozygotes exhibit higher detection thresholds and lower suprathreshold bitterness for PROP compared to
[...] Read more.
Bitterness from phenylthiocarbamide and 6-n-propylthiouracil (PROP) varies with polymorphisms in the
TAS2R38 gene. Three SNPs form two common (AVI, PAV) and four rare haplotypes (AAI, AAV, PVI, and PAI). AVI homozygotes exhibit higher detection thresholds and lower suprathreshold bitterness for PROP compared to PAV homozygotes and heterozygotes, and these differences may influence alcohol and vegetable intake. Within a diplotype, substantial variation in suprathreshold bitterness persists, and some AVI homozygotes report moderate bitterness at high concentrations. A second receptor encoded by a gene containing a functional polymorphism may explain this. Early work has suggested that PROP might activate TAS2R4 in vitro, but later work did not replicate this. Here, we identify three
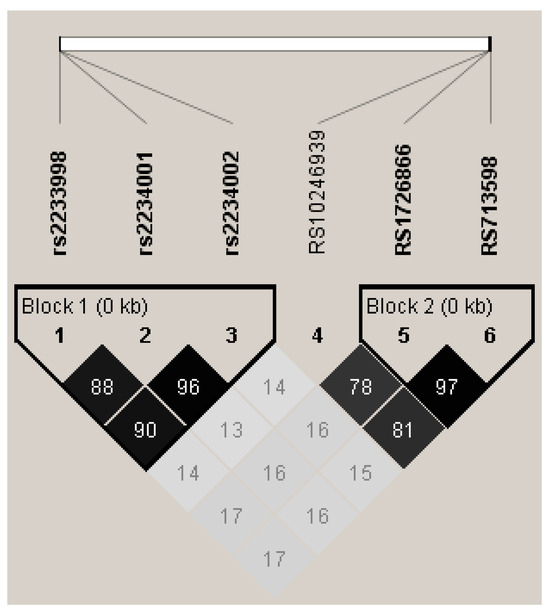
TAS2R4 SNPs that result in three diplotypes—SLN/SLN, FVS/SLN, and FVS/FVS—which make up 25.1%, 44.9%, and 23.9% of our sample. These
TAS2R4 haplotypes show minimal linkage disequilibrium with
TAS2R38, so we examined the suprathreshold bitterness as a function of both. The participants (
n = 243) rated five PROP concentrations in duplicate, interleaved with other stimuli. As expected, the
TAS2R38 haplotypes explained ~29% (
p < 0.0001) of the variation in the bitterness ratings, with substantial variation within the haplotypes (AVI/AVI, PAV/AVI, and PAV/PAV). Notably, the
TAS2R4 diplotypes (independent of the
TAS2R38 haplotypes) explained ~7–8% of the variation in the bitterness ratings (
p = 0.0001). Given this, we revisited if PROP could activate heterologously expressed TAS2R4 in HEK293T cells, and calcium imaging indicated 3mM PROP is a weak TAS2R4 agonist. In sum, our data are consistent with the second receptor hypothesis and may explain the recovery of the PROP tasting phenotype in some AVI homozygotes; further, this finding may potentially help explain the conflicting results on the
TAS2R38 diplotype and food intake.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT