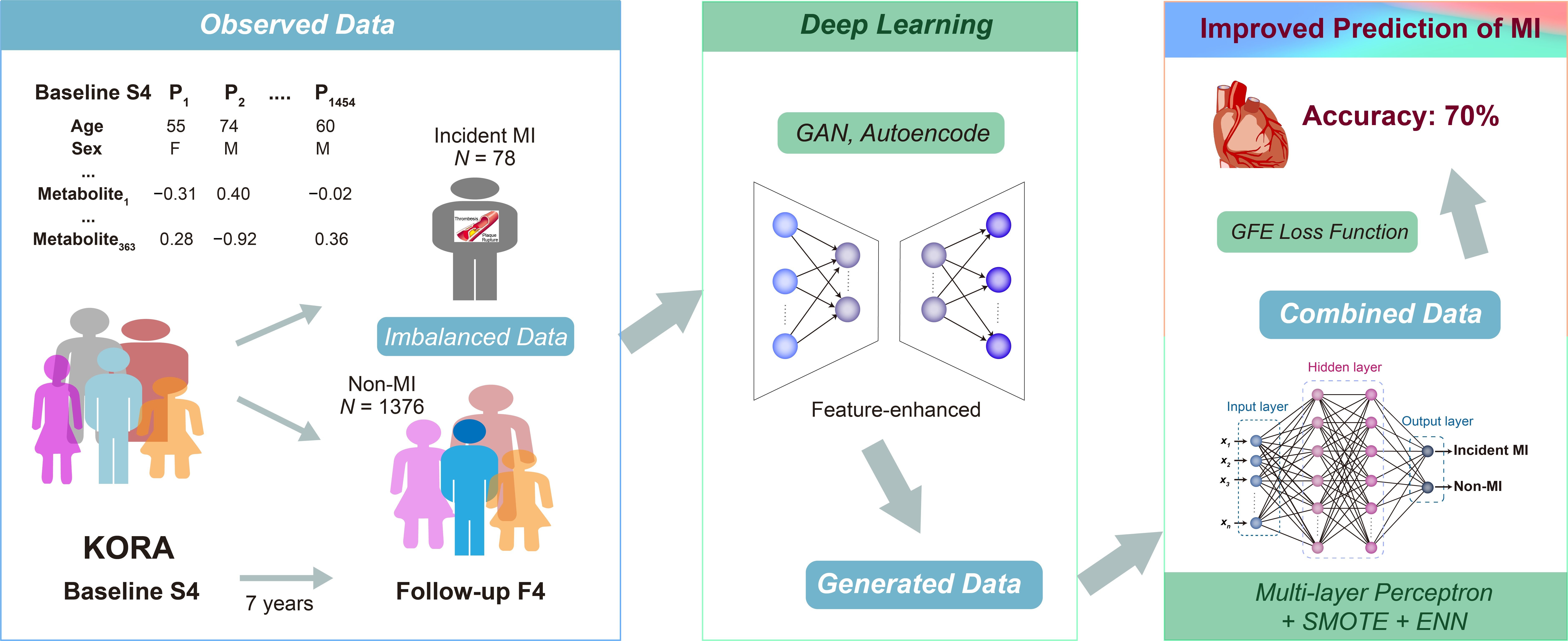
The aim of this paper was to evaluate the fracture resistance of 3D-printed zirconia occlusal veneers (OVs) of different thicknesses and supported by different abutment materials.
Materials and Methods: The standard OV of a natural molar was prepared and digitized using a laboratory 3D scanner. The resulting digital tooth abutment was milled either using cobalt–chromium (CoCr) or a fiber-reinforced composite (FRC). All the abutments were digitized and standardized OVs (30° tilt of all the cusps) designed with 0.4 mm, 0.6 mm, or 0.8 mm wall thicknesses. The OVs were fabricated using either the Programill PM7 milling device (Ivoclar Vivadent, PM) or one of two 3D zirconia printers, Cerafab 7500 (Lithoz, LC) or Zipro-D (AON, ZD). The ZD samples were only tested on CoCr abutments. The completed OVs were luted to their abutments and subjected to artificial aging, consisting of thermocycling and chewing simulation before fracture testing with a steel sphere (d = 8 mm) as an antagonist with three contact points on the occlusal OV surface. Besides the total fracture resistance F
u,tot, the lowest contact force F
u,cont leading to the local fracture of a cusp was of interest. The possible effects of the factors fabrication approach, wall thickness, and abutment material were evaluated using ANOVA (α = 0.05; SPSS Ver.28).
Results: The total fracture resistance/contact forces leading to failure ranged from F
u,tot = 416 ± 83 N/F
u,cont = 140 ± 22 N for the 0.4 mm OVs fabricated using LC placed on the FRC abutments to F
u,tot = 3309 ± 394 N (ZD)/F
u,cont = 1206 ± 184 N (PM) for the 0.8 mm thick OVs on the CoCr abutments. All the factors (the fabrication approach, abutment material, and OV wall thickness) had an independent effect on F
u,tot as well as F
u,cont (
p < 0.032). In pairwise comparisons for F
u,tot of the OVs luted to the CoCr abutments, the ZD samples statistically outperformed the LC- and PM-fabricated teeth irrespective of the thickness (
p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Within the limitations of this study, the printed occlusal veneers exhibited comparable fracture resistances to those of the milled variants. However, more resilient abutments (FRC as a simulation of dentine) as well as a thinner wall thickness led to reduced OV fracture resistance, suggesting that 0.4 mm thick zirconia OVs should not be unreservedly used in every clinical situation.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT