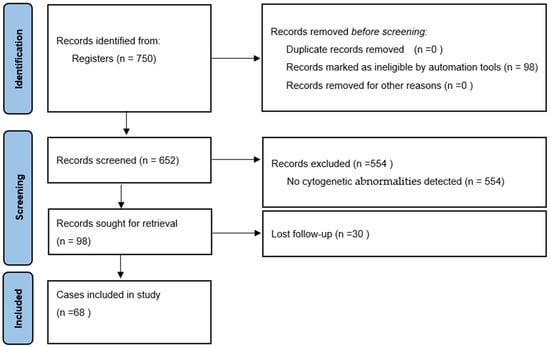
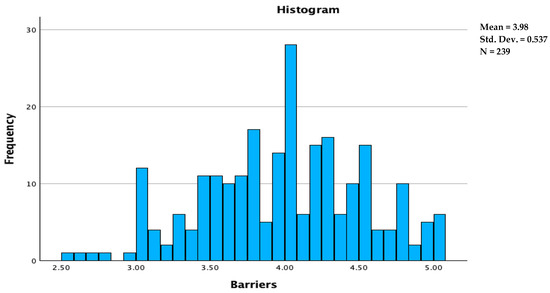
The industrialization of Fe-based amorphous alloys with high a saturation magnetic flux density (
Bs) has been limited so far due to their inadequate amorphous forming ability (AFA). In this study, the effects of substituting Si with C on the AFA,
[...] Read more.
The industrialization of Fe-based amorphous alloys with high a saturation magnetic flux density (
Bs) has been limited so far due to their inadequate amorphous forming ability (AFA). In this study, the effects of substituting Si with C on the AFA, thermal stability, and magnetic properties of Fe
82Si
6−xB
9P
3C
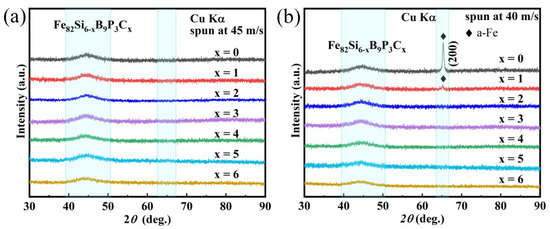
x (x = 0–6) alloys were systematically investigated. The experimental results demonstrate that the AFA, thermal stability, and soft magnetic properties can be significantly enhanced by the addition of C. Specifically, at a copper wheel velocity of 40 m/s, the Fe
82Si
6−xB
9P
3C
x (x = 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6) alloy ribbons exhibit a fully amorphous structure in the as-spun state. The activation energy required for the α-Fe phase crystallization process in Fe
82Si
6−xB
9P
3C
x (x = 0, 2, 4, and 6) alloys is determined to be 326.74, 390.69, 441.06, and 183.87 kJ/mol, respectively. Among all of the compositions studied, the Fe
82Si
4B
9P
3C
2 alloy exhibits optimized soft magnetic properties, including a low coercivity (
Hc) of 1.7 A/m, a high effective permeability (
μe) of 10608 (
f = 1 kHz), and a relatively high Bs of 1.61 T. These improvements may be attributed to a more homogeneous and optimized magnetic domain structure being achieved through proper C addition. This work holds significant implications for the advancement of Fe-based soft magnetic amorphous alloys with high
Bs.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT