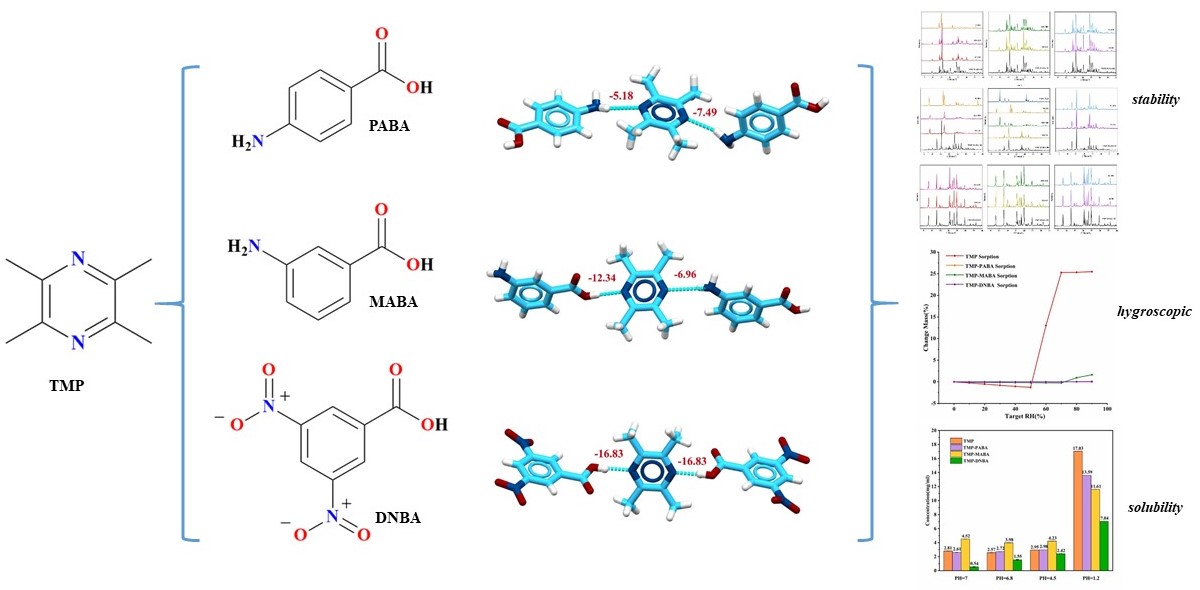
Introduction and Hypothesis: Obstetric anal sphincter injuries (OASIs) complicate 5.8% of vaginal deliveries. Our objective was to assess if the primary delivery provider, a nurse-midwife versus physician obstetrician, is associated with OASIs. Methods: We performed a secondary analysis of the
Consortium of Safe Labor, a multicenter, retrospective cohort study. Included were nulliparous women with singleton, vaginal delivery at ≥37 weeks from 2002 to 2008. Women were excluded if delivery was complicated by shoulder dystocia or from sites without midwife deliveries. Student’s
t-tests, chi-squared analysis, and Fisher’s exact test were used as appropriate. Multivariable logistic regression and propensity score-matching analyses were performed. Results: Of 228,668 births at 19 sites, 2735 births from 3 sites met the inclusion criteria: 1551 physician and 1184 midwife births. Of all births, 4.2% (
n = 116) were complicated by OASIs. Physician patients were older, more often White, privately insured, with higher BMI, more medical co-morbidities, and labor inductions/augmentations. Midwife patients had higher fetal gestational age and infant birth weights (all
p < 0.05). OASIs were more common in physician compared to midwife births (5.9% vs. 2.0%,
p < 0.0001). This difference persisted in multivariable logistic regression. OASIs were 2.4 (95%CI 1.5–3.9) times more likely with physician delivery when controlling for maternal heart disease, episiotomy, increasing maternal age, decreasing maternal BMI, non-White race, and increasing birthweight. The AUC was 0.78. With propensity score matching, OASI rates remained higher amongst physician births (6.6% vs. 1.8%,
p < 0.0001; aOR 3.8 (95%CI 2.0–7.1)). Conclusion: OASIs were more common in physician compared to midwife deliveries even when controlling for other associated factors.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT