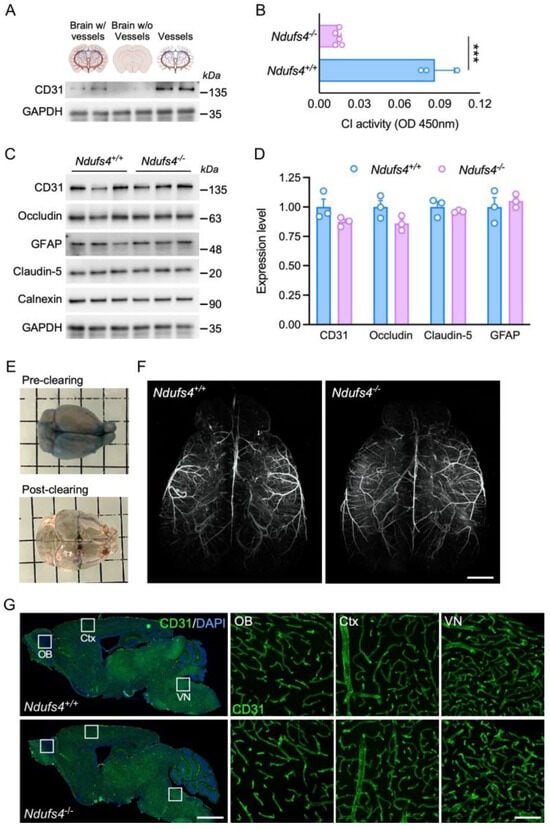
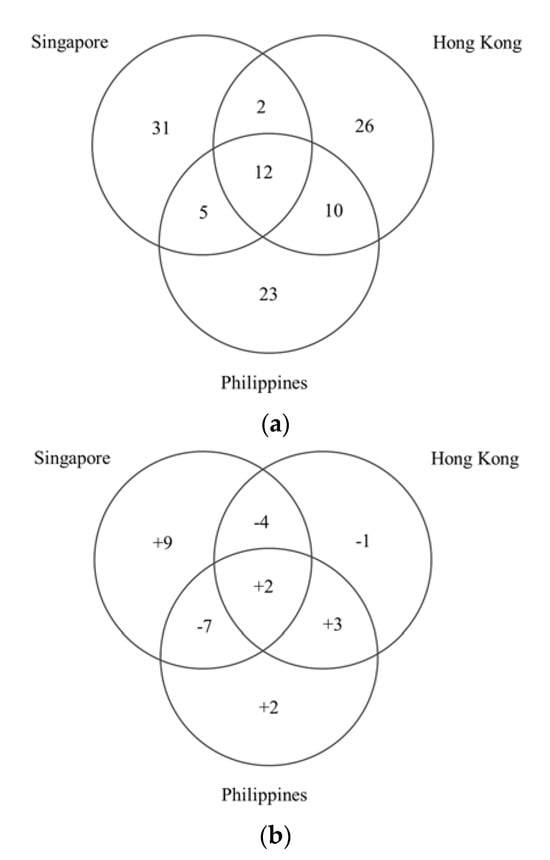
Colored varieties of turkeys, such as the broad-breasted Bronze, not currently subject to intensive breeding work, are kept only in amateur breeding and treated rather as ornamental poultry. They are raised in extensive systems, which undoubtedly affects the quality of the meat obtained.
[...] Read more.
Colored varieties of turkeys, such as the broad-breasted Bronze, not currently subject to intensive breeding work, are kept only in amateur breeding and treated rather as ornamental poultry. They are raised in extensive systems, which undoubtedly affects the quality of the meat obtained. Consumers are looking for meat with specific and unique sensory qualities; hence, the interest in meat from turkeys with a slower-than-typical growth rate, such as the broad-breasted Bronze, is justified. The object of this research was to analyze the physicochemical properties and nutritional value (amino acid, fatty acid, and antioxidant profile) of the breast and thigh muscles of broad-breasted Bronze turkeys with regard to gender. It was shown that gender had little effect on muscle chemical composition, amino acid, and fatty acid content (
p > 0.05), as well as most oxido-reduction indices. However, significant differences were noted in muscle quality traits such as color brightness (L*; turkeys > indors;
p = 0.023), proportion of red (a*; turkeys < indors;
p = 0.048) and yellow (b*; turkeys > indors;
p = 0.039), and water absorption (turkeys < indors;
p = 0.009). The type of muscle also had a significant effect on quality characteristics. Higher a*, b*, C*, pH, water absorption, and thermal leakage were shown in the femoral muscle (
p < 0.001), while L* and h were higher in the pectoral muscle (
p < 0.001). Turkey meat was characterized by a high proportion of unsaturated fatty acids (MUFA + PUFA ~68%), favorable FA index values, and low lipid oxidation indices. Thigh muscles (especially turkey) were more caloric, and contained significantly (
p < 0.001) more fat and all major FA groups. Breast muscles (especially of turkeys) were characterized by a high protein content (about 25%) and a high proportion of essential amino acids. The data obtained indicate that broad-breasted Bronze turkeys can provide high-quality meat, and are an excellent option for meeting modern consumer needs.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT