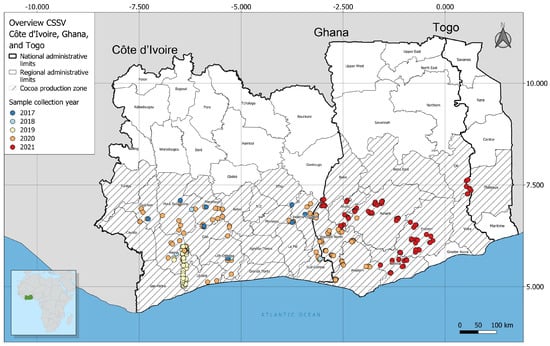
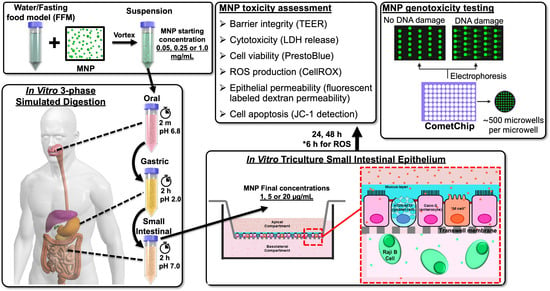
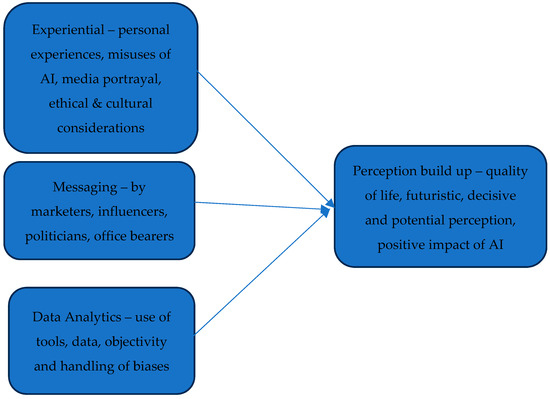
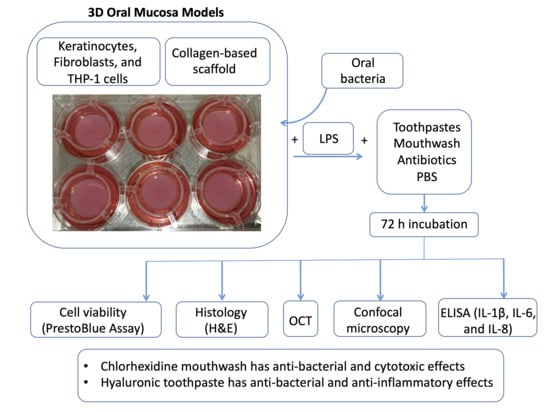
Adaptive characteristics of plants, such as those associated with photosynthesis and resource use efficiency, are usually affected by synthesis costs and resource availability. The impact of extreme climate events such as long-term drought on plant physiological functions needs to be examined, particularly as
[...] Read more.
Adaptive characteristics of plants, such as those associated with photosynthesis and resource use efficiency, are usually affected by synthesis costs and resource availability. The impact of extreme climate events such as long-term drought on plant physiological functions needs to be examined, particularly as it concerns the internal management of water and nitrogen (N) resources. In this study, we evaluated the resource management strategies for water and N by xerophytic shrubs,
Artemisia ordosica and
Salix psammophila, under extreme summer drought. This was carried out by comparing the plants’ physiological status during periods of wet and dry summer conditions in 2019 and 2021. Compared with the wet period,
A. ordosica and
S. psammophila both decreased their light-saturated net carbon (C) assimilation rate (
Asat), stomatal conductance (
gs), transpiration rate (
E), leaf N content per leaf area (
Narea), and photosynthetic N use efficiency (PNUE) during the summer drought. Whether in wet or dry summers, the gas-exchange parameters and PNUE of
A. ordosica were generally greater than those associated with
S. psammophila. The instantaneous water use efficiency (IWUE) response to drought varied with species. As a drought-tolerant species, the
A. ordosica shrubs increased their IWUE during drought, whereas the
S. psammophila shrubs (less drought-tolerant) decreased theirs. The divergent responses to drought by the two species were largely related to differences in the sensitivity of
gs, and as a result,
E. Compared with
A. ordosica,
S. psammophila’s inferior plasticity regarding
gs response affected its ability to conserve water during drought. Our research illustrates the need for assessing plasticity in
gs when addressing plant adaptation to long-term drought. A high dry-season IWUE in xerophytic shrubs can benefit the plants by augmenting their C gain.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT