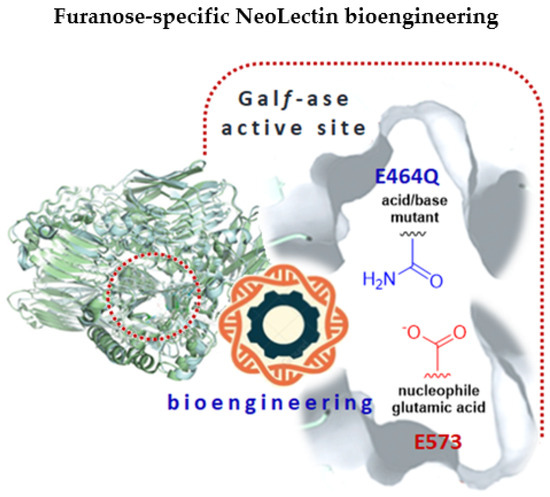
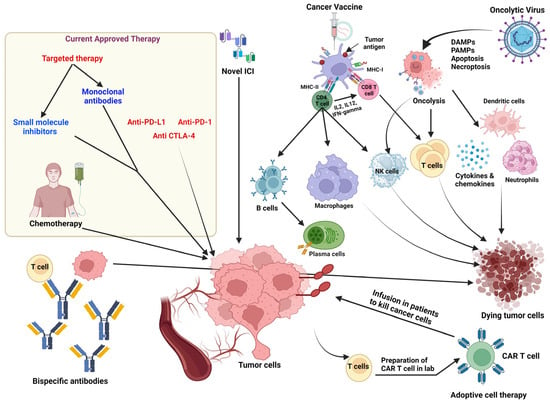
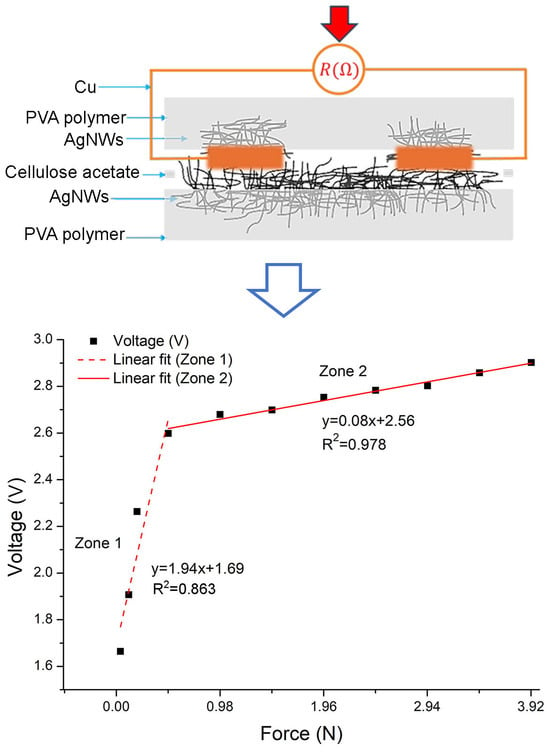
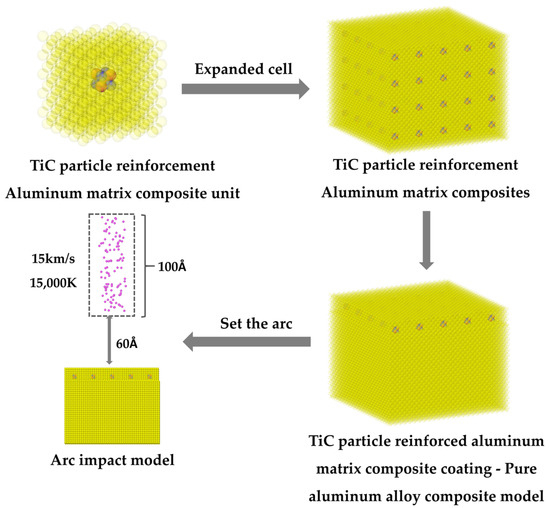
Two experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of isobutyramide (IBA) and slow-release urea (SRU) as substitutes for soybean meal (SBM) in the finishing diet of beef cattle. The completely randomized design in vitro experiment with five treatments, i.e., control, 0.9% SRU group,
[...] Read more.
Two experiments were conducted to investigate the effects of isobutyramide (IBA) and slow-release urea (SRU) as substitutes for soybean meal (SBM) in the finishing diet of beef cattle. The completely randomized design in vitro experiment with five treatments, i.e., control, 0.9% SRU group, 0.6% SRU + 0.3% IBA group (SRU-I), 0.3% SRU + 0.6% IBA group (IBA-S), 0.9% IBA group was conducted. The results showed that the IBA-S and IBA increased (
p ≤ 0.05) substrate disappearance of dry matter (DM), neutral detergent fiber (NDF), acid detergent fiber (ADF), total gas, and total volatile fatty acids (TVFA). The SRU group had the highest (
p < 0.01) crude protein disappearance and ammonia nitrogen concentration, but the IBA contrarily decreased (
p < 0.01) them compared with the control. Inclusion of IBA increased isobutyrate concentrations (
p = 0.01) with the highest value for the IBA group. Then, an 84-day replicate 4 × 4 Latin square design with 8 Angus steers and four treatments, i.e., control, SRU, SRU-I, IBA-S was performed. The results showed that the treatments did not affect DM intake (
p > 0.05) but tended (
p = 0.09) to increase average daily gain. The inclusion of IBA increased (
p < 0.05) the apparent digestibility of DM, organic matter, NDF, ADF, TVFA, and microbial crude protein with the highest values for the IBA-S group. The IBA-contained groups also increased (
p ≤ 0.01) isobutyrate concentration, activities of carboxymethyl cellulase and xylanase, and the relative abundance of
Butyrivibrio fibrisolvens with the highest values for the IBA-S group. The SRU had no effect on animal growth and nutrient apparent digestibility. In conclusion, IBA was developed as a new substitute for SBM in the finishing diet of beef cattle, and the optimal strategy was the isonitrogenous substitution of SBM with 0.3% SRU and 0.6% IBA of the diet.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT