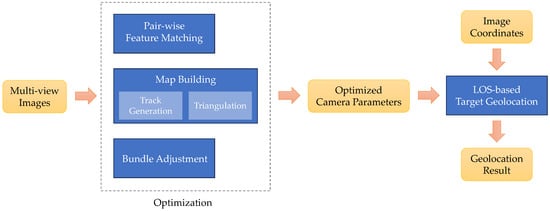
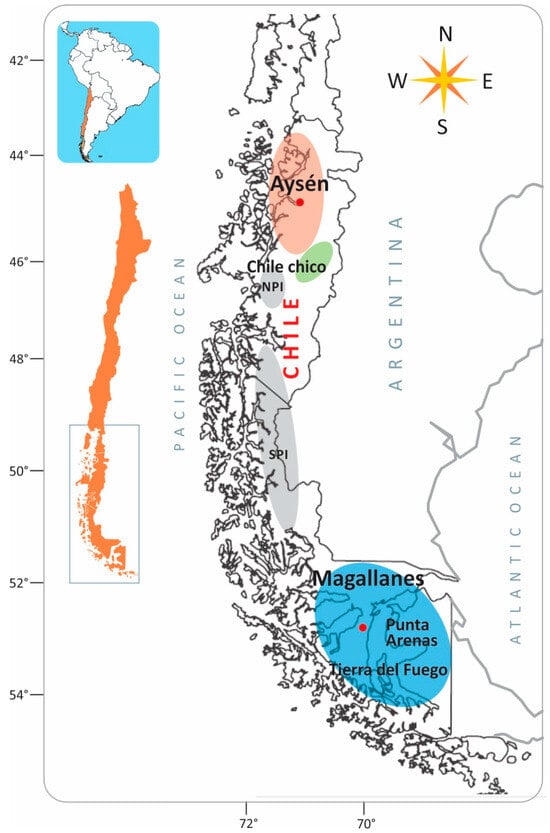
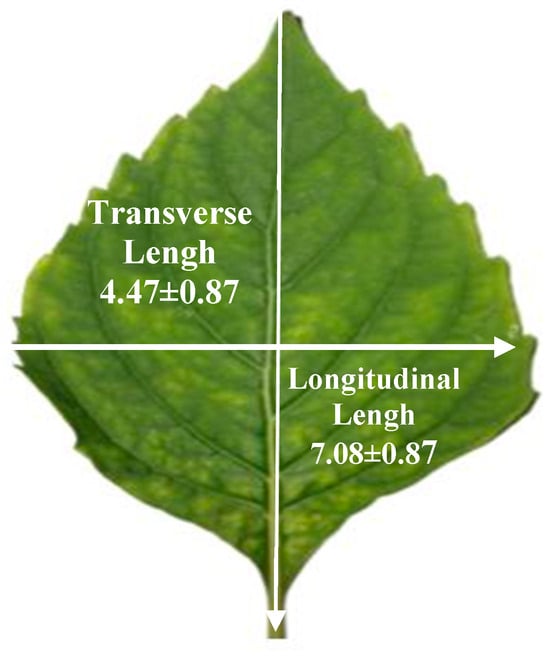
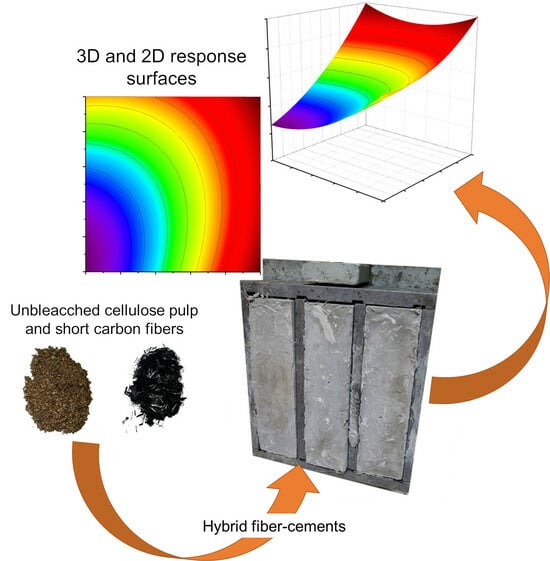
Denture stomatitis (DS) is a very common disease in wearers of removable complete and partial dentures with a worldwide prevalence in the range of 20–67%. Both industrially developed and impoverished nations are affected by the illness. DS is often associated with ill-fitting dentures or a fungal infection with
Candida spp.
Candida is normally found in the oral cavity microbiota, but it can be harmful to the health of elderly people with underlying diseases. Therefore, the purpose of the present study is to offer the most recent information about the epidemiology, etiology, and global distribution of
Candida species associated with DS through a systematic review. Several databases, including Medline, Web of Science, and Scopus, were used to conduct an extensive search of the literature published in the previous 20 years. The selection of studies was performed by two authors. The extracted data were as follows: author, year of publication, country, sample, frequency of DS, method of diagnosing stomatitis, species of
Candida, risk factors, and etiology of the disease. The JBI Critical appraisal tools were used to assess the quality of the studies. Eventually, twenty-eight studies were included in the systematic review. Twenty-one studies investigated DS, while seven studies examined
Candida colonization in patients using removable dentures. The results show that the main causes of DS include the type of dentures, continuous wearing of dentures, and the formation of a
Candida biofilm, which is facilitated by poor dental hygiene. Additionally, previous studies have pinpointed the significance of the salivary flow, saliva composition, and salivary pH. The findings of the current review indicate that it is crucial to monitor denture wearers for the appearance of DS, especially the patients whose immunity has been impaired due to a systemic condition. Finally, frequent follow-ups should include a clinical examination and microbial swabs of the palatal mucosa and the mucosal surface of the denture.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT