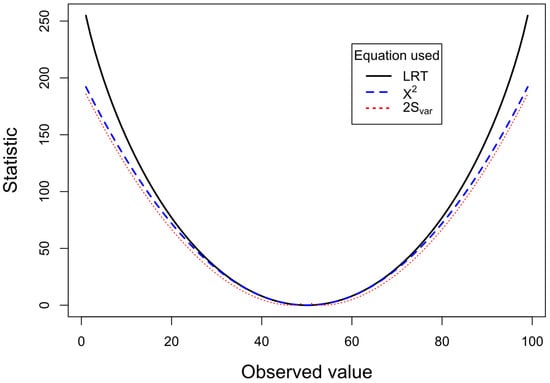
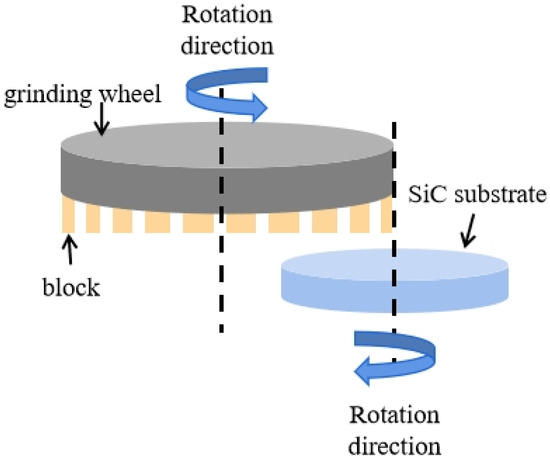
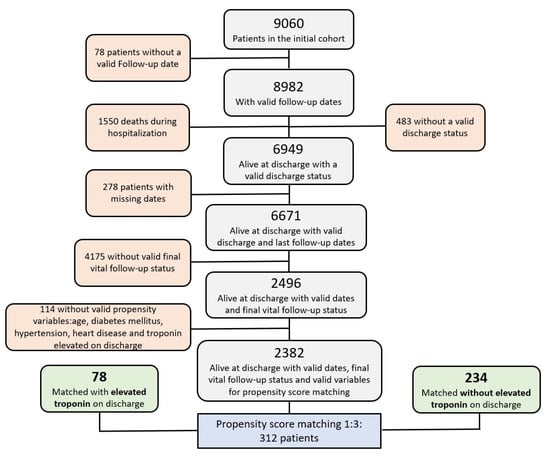
This study aims to investigate the effects of parent rock and minerals on lateritic weathering. The study presents X-ray diffraction (XRD), whole-rock geochemistry, and Nd-Sr isotopic data for examining two profiles, 10 and 12 m thick, respectively, that illustrate the regional tropical weathering status in the Midwest of Brazil. The profiles, developed from metasedimentary and sedimentary rocks, are constituted by saprolite, mottled horizon, lateritic duricrust, and oxisol. Across the profiles, the minerals controlling the weathering geochemistry are muscovite, microcline, quartz, kaolinite, hematite, goethite, and gibbsite. Red and yellow zones in the saprolite and mottled horizon as well as the lateritic duricrust with breccia/fragmental, pisolitic, and oolitic textures make profile 1 more complex. In contrast, profile 2 has an oxisol that mantles the homogeneous vermiform lateritic duricrust. Fe
2O
3, accumulated during surface weathering, is a potent element in the geochemical profile control since it forms the harder goethite to hematite lateritic duricrust, bearing most of the trace elements (As, Cu, Cs, Pb, Sc, Sr, Th, U, V, and Zn) with similar ionic radii and electrovalence. The LREE have affinity for the elements of the Fe
2O
3 group of the lateritic duricrust. On the other hand, the K
2O group together with Zr and TiO
2 e in the phyllite, saprolite, and mottled horizon of profile 1, are associated with the HREE. Additionally, in profile 2, the HREE are mostly associated with the Al
2O
3 group and the residual minerals in the oxisol. The indication that REE is associated with phosphates, zircon, rutile/anatase, cereanite, and muscovite/illite, which have variable weathering behavior, caused the REE fractionation to occur across and between the profiles. Despite the REE fractionation, the Ɛ
Nd(0) values along the profiles consistently maintain the signature of the parent rock. Muscovite and microcline weathering, in profiles 1 and 2, respectively, control the decrease in
87Sr/
86Sr signatures of both profiles and the distinct radiogenic ratios. The development of lateritic duricrust in both profiles indicates a similar weathering intensity, although the gibbsite–kaolinite predominance in the oxisol of profile 2 highlights a geochemical reorganization under humid conditions, as well as near-intense soluble silica leaching.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT