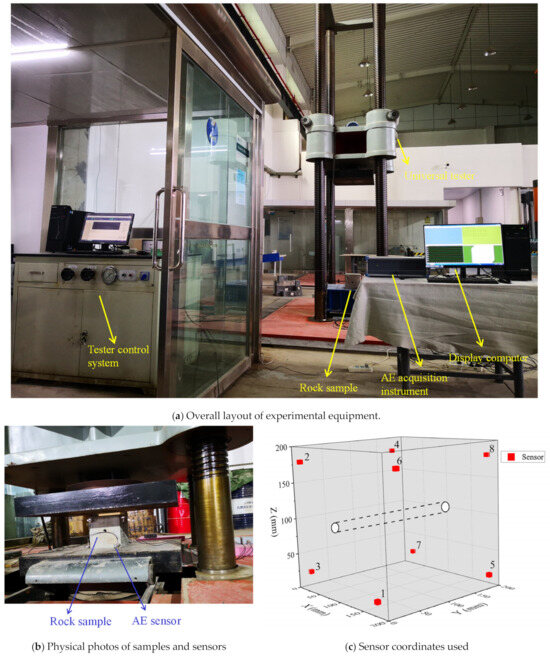
In this study, the antifungal activity of cumin seed oil (CSO) was tested on
Fusarium graminearum. (i) Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) and related concentrations (IC
75, IC
50, and IC
25) were detected; (ii) toxicity was evaluated by a
[...] Read more.
In this study, the antifungal activity of cumin seed oil (CSO) was tested on
Fusarium graminearum. (i) Minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) and related concentrations (IC
75, IC
50, and IC
25) were detected; (ii) toxicity was evaluated by a water-soluble tetrazolium salt-1 (WST-1) assay; (iii) genomic/epigenomic alterations were evaluated by the coupled restriction enzyme digestion-random amplification (CRED-RA) method; (iv) oxidative stress was investigated by
CAT expression, catalase activity, and DCF-DA staining; (v) deoxynivalenol biosynthesis was evaluated by
tri6 expression; (vi) and potential effects of CSO on wheat were tested by a water loss rate (WLR) assay. MIC, IC
75, IC
50 and IC
25 values were detected at 0.5, 0.375, 0.25, and 0.125 mg mL
−1. In WST-1 assays, significant decreases (
p < 0.001) were detected. Genomic template stability (GTS) related to methylation differences ranged from 94.60% to 96.30%. Percentage polymorphism for
HapII/
MspI values were as 9.1%/15.8%.
CAT (oxidative stress-related catalase) and
tri6 (zinc finger motif transcription factor) gene expressions were recorded between 5.29 ± 0.74 and 0.46 ± 0.10 (
p < 0.05). Increased catalase activity was detected (
p < 0.05) by spectrophotometric assays. DCF-DA-stained (oxidative stressed) cells were increased in response to increased concentrations, and there were no significant changes in WLR values. It was concluded that CSO showed strong antifungal activity on
F. graminearum via different physiological levels.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT