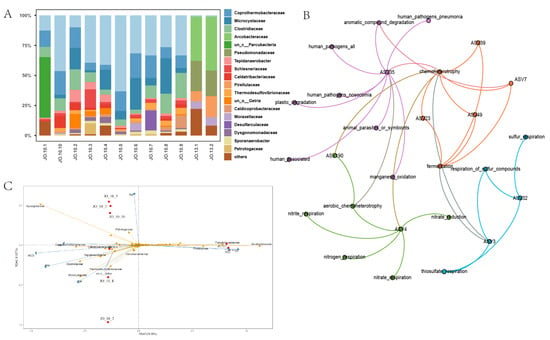
Algal blooms caused by eutrophication are a major global problem, and the monitoring and prediction of algal densities in lakes are important indicators of eutrophication management. However, the reliability of the commonly used chlorophyll-
a (Chl-
a) to characterize phytoplankton density in lake environments needs to be further investigated. In this paper, we sampled and analyzed 365 samples from nine plateau lakes in Yunnan Province during the dry and rainy seasons. The Chl-
a data measured by the laboratory spectrophotometric method and the portable YSI multi-parameter water quality meter (YSI) directly used in the field were compared, and regression analysis and correlation analysis with phytoplankton density were performed. Most of the Chl-
a values measured by the laboratory instrument were greater than those measured by the YSI, and the correlation between the two methods was weak (0.492,
p < 0.001). The correlation between Chl-
a and phytoplankton density measured by the YSI reached 0.67 (
p < 0.001) in the dry season, while the laboratory methods used to measure Chl-
a to characterize phytoplankton density may have led to an overestimation of phytoplankton density due to nonspecific sources of Chl-
a. However, both methods are relatively inaccurate for characterizing phytoplankton density. For different trophic states of lakes, nutrient concentration changes affect the Chl-
a concentration of phytoplankton. During different seasons, changes in the fluorescence intensity of phytoplankton in response to environmental conditions prevent the YSI results from reflecting the authentic phytoplankton density. Furthermore, high species diversity can lead to inconsistent changes in Chl-
a and phytoplankton because the content of Chl-
a in individual cells of different phytoplankton is different. The relationship between Chl-
a and phytoplankton density was species specific. Therefore, when applying Chl-
a to characterize phytoplankton density in lakes, it is necessary to consider environmental conditions, phytoplankton community structure and other practical conditions. In addition, laboratory analytical methods and instrumental techniques and instruments need to be improved.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT