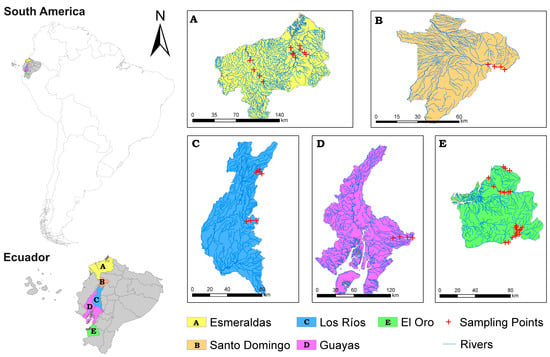
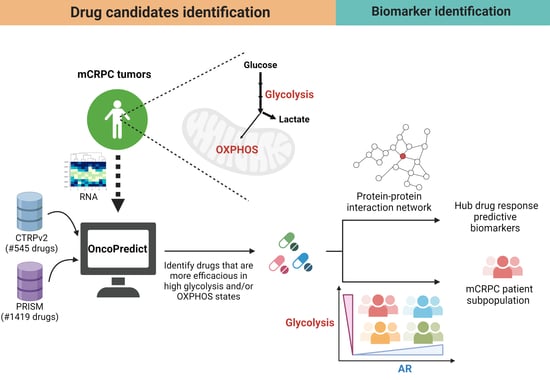
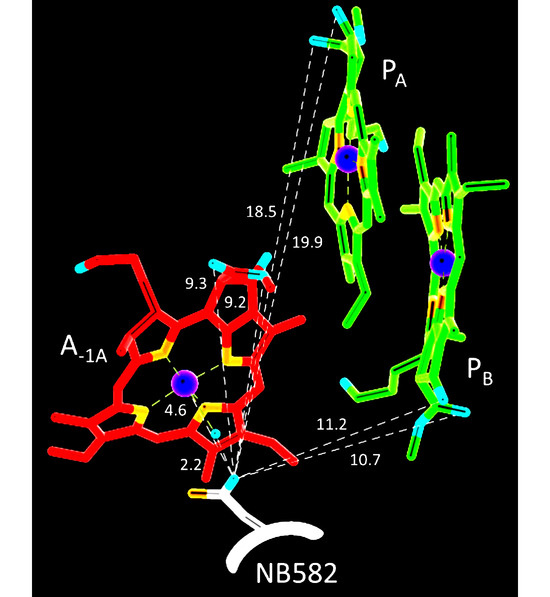
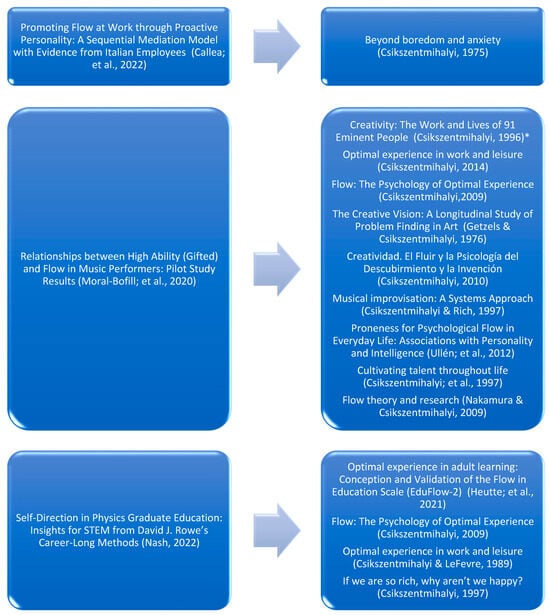
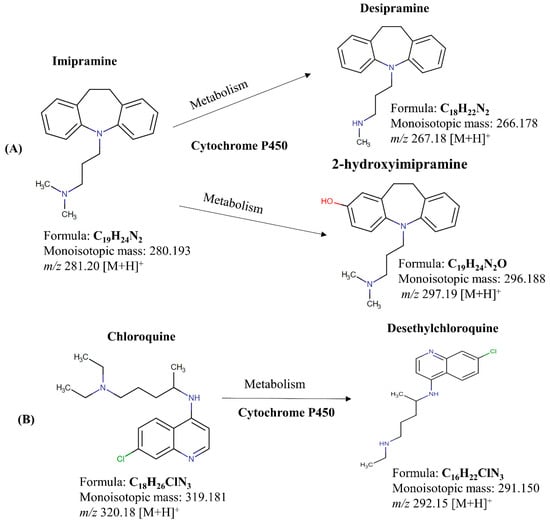
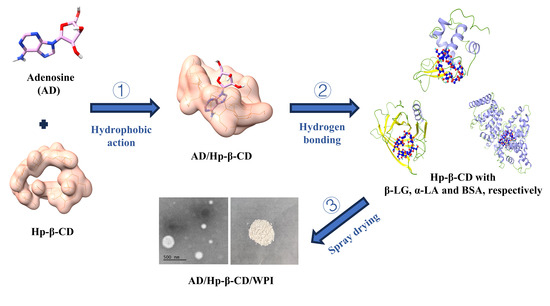
Background: Pitt–Hopkins syndrome (PTHS) is a rare genetic disorder affecting psychomotor, social, and intellectual development, caused by a mutation in the
TCF4 gene. The study aims to gather the phenotype and genotype data of PTHS patients from Poland and to assess the
[...] Read more.
Background: Pitt–Hopkins syndrome (PTHS) is a rare genetic disorder affecting psychomotor, social, and intellectual development, caused by a mutation in the
TCF4 gene. The study aims to gather the phenotype and genotype data of PTHS patients from Poland and to assess the quality of life (QoL) and the impact of the disorders on the family.
Methods: Eight families with PTHS participated in the study. To obtain data, the following standardized questionnaires were used: Questionnaire on Clinical Problems (QCP), the PedsQL™ Family Impact Module, and the QL-Disability Questionnaire. Additionally, a retrospective analysis of clinical examination, genetic consult, medical history, and genotype of each individual was performed.
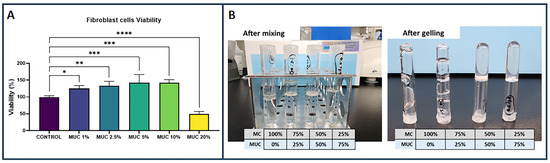
Results: All of the examined children exhibited a mutation in the
TCF4 gene and typical features of PTHS. The most prevalent clinical symptoms in the study group included typical PTHS appearance, intellectual disability (
n = 5; as the rest of the patients were too young to be assessed), abnormal speech development (
n = 8), reduced pain response (
n = 7), constipation (
n = 7), drooling (
n = 7), cold extremities (
n = 7), and disturbances in sensory integration processes (
n = 7). The QL-Disability Questionnaire revealed a total QoL score of 67.7/100 for children with PTHS, while the QoL for their families in the PedsQL Family Impact Module was 53.82/100. The highest-rated domain was cognitive functioning (Median (Me) = 67.50; Standard Deviation (SD) = 21.95), while the lowest was daily activities (Me = 25.00; SD = 29.86).
Conclusions: The study allowed the collection of data on the phenotype and genotype of children with PTHS living in Poland. Overall, our study showed that the QoL of children with PTHS is impaired.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT