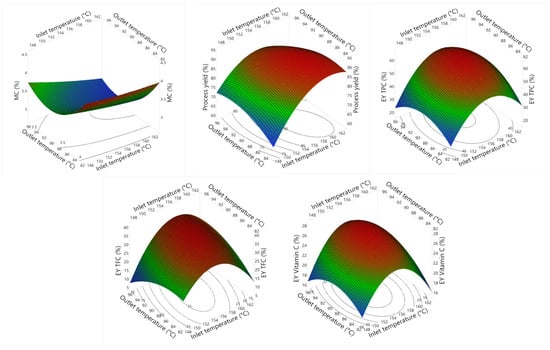
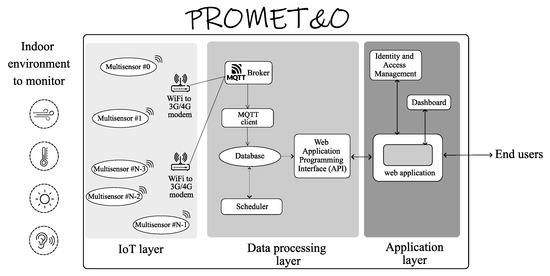
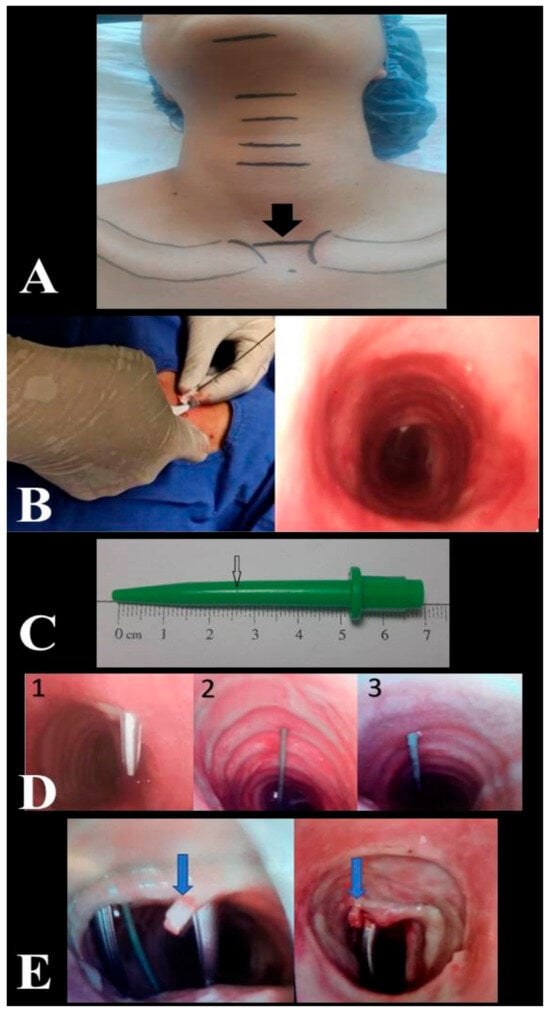
A high-efficiency nickel-doped porous biochar (PCNi
3) has been successfully synthesized from chestnut shell waste via a two-step chemical activation treatment with H
3PO
4. The influences of microstructure, surface morphology, elemental composition, surface functional groups, specific surface area, porosity,
[...] Read more.
A high-efficiency nickel-doped porous biochar (PCNi
3) has been successfully synthesized from chestnut shell waste via a two-step chemical activation treatment with H
3PO
4. The influences of microstructure, surface morphology, elemental composition, surface functional groups, specific surface area, porosity, pore-size distribution, and chemical properties of the surface state on the removal of Cr (VI) from water were thoroughly investigated by using XRD, FESEM, FTIR, Raman, BET, and XPS testing methods, N
2 adsorption, and XPS testing techniques respectively. The results indicate that the treatment of H
3PO
4 activation and nickel doping can effectively improve microstructure characteristics, thus promoting Cr (VI) adsorption capacity. The effects of initial solution pH, solution concentration, time, and temperature on remediation are revealed. The Cr (VI) uptake experiments imply that the adsorption curves of PCNi
3 fit well with the Freundlich model, the pseudo-second-order kinetic model, and the Elovich model. The adsorption process of PCNi
3 can be regarded as a spontaneous endothermic reaction limited by diffusion among particles and porosity. The adsorption mechanisms of PCNi
3 are ion exchange, complexation, electrostatic adsorption, and coprecipitation with the assistance of surface active sites, porosity, Ni
0 particles, and Ni
7P
3. With these advantages, PCNi
3 reveals an extraordinary Cr (VI) removal capacity and a strong ability to reduce Cr (VI) to Cr (III).
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT