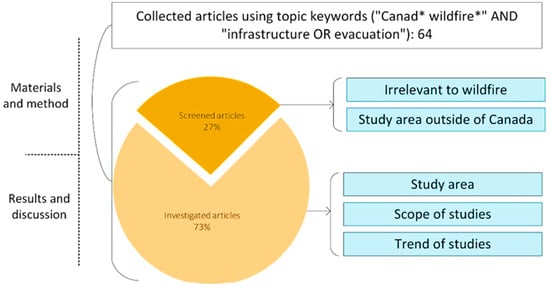
Water resource management has emerged as a pivotal concern within arid regions in recent times. The water footprint (WFP) index stands out as a principal gauge for facilitating comprehensive watershed management. This study endeavors to compute the WFP of diverse agricultural products encompassing major crops, orchards, cucurbits, and medicinal plants across arid regions. This research focuses on three distinct climate scenarios: the Shazand Plain with a semidry climate, the Khomein Plain characterized by a dry climate, and the Saveh Plain exhibiting a very dry climate. This study also seeks to ascertain the climate most conducive to cultivating crops from a WFP (green, blue, and gray) perspective. To achieve these objectives, this study employed the CropWat family software to determine crop water requirements, as well as considering crop yield and relevant parameters for calculations. The findings of the investigation unveiled that the cultivated areas in the respective climates amounted to 19,479 ha (semidry), 18,166 ha (dry), and 41,682 ha (very dry). These areas were allocated as follows: 88%, 85%, and 55% for crops; 11%, 13%, and 40% for orchards; and 1%, 2%, and 5% for cucurbit crops. Importantly, the very dry climate was predisposed to allocating more land for low-water-demand orchards. Among the major crops, wheat occupied 44%, 39%, and 43% of the total areas in the semidry, dry, and very dry climates, respectively. Analyzing the overall agricultural output in these climates, it was revealed that over 79%, 69%, and 66% of production correlated with crops; 17%, 19%, and 22% with orchards; and 4%, 12%, and 12% with cucurbits, respectively. In terms of water consumption, maize and apples emerged as the highest performers, with varying consumption patterns across different crops. Interestingly, canola exhibited a substantially higher WFP, surpassing wheat and barley by 56.48% and 58.85%, respectively, in dry climates. Cucurbit crops, on the other hand, displayed a lower WFP in dry climates, which could potentially encourage their cultivation. The influence of climate warming on canola’s
WFPgray introduced complexity, challenging the conventional correlation between WFP and yields. Medicinal plants consistently demonstrated lower WFP values, underscoring the need for deliberate and considerate cultivation decisions in this regard.
Full article
 IJMS
IMPACT
IJMS
IMPACT Applied Sciences
IMPACT
Applied Sciences
IMPACT Sustainability
IMPACT
Sustainability
IMPACT Sensors
IMPACT
Sensors
IMPACT JCM
IMPACT
JCM
IMPACT Materials
IMPACT
Materials
IMPACT Molecules
IMPACT
Molecules
IMPACT Energies
IMPACT
Energies
IMPACT Electronics
IMPACT
Electronics
IMPACT Remote Sensing
IMPACT
Remote Sensing
IMPACT Cancers
IMPACT
Cancers
IMPACT Nutrients
IMPACT
Nutrients
IMPACT Mathematics
IMPACT
Mathematics
IMPACT Foods
IMPACT
Foods
IMPACT Buildings
IMPACT
Buildings
IMPACT Polymers
IMPACT
Polymers
IMPACT Animals
IMPACT
Animals
IMPACT Water
IMPACT
Water
IMPACT Plants
IMPACT
Plants
IMPACT Agronomy
IMPACT
Agronomy
IMPACT Biomedicines
IMPACT
Biomedicines
IMPACT Processes
IMPACT
Processes
IMPACT Microorganisms
IMPACT
Microorganisms
IMPACT Diagnostics
IMPACT
Diagnostics
IMPACT Nanomaterials
IMPACT
Nanomaterials
IMPACT Viruses
IMPACT
Viruses
IMPACT Medicina
IMPACT
Medicina
IMPACT Healthcare
IMPACT
Healthcare
IMPACT Cells
IMPACT
Cells
IMPACT Forests
IMPACT
Forests
IMPACT Agriculture
IMPACT
Agriculture
IMPACT Land
IMPACT
Land
IMPACT JMSE
IMPACT
JMSE
IMPACT IJERPH
IJERPH
 Symmetry
IMPACT
Symmetry
IMPACT Genes
IMPACT
Genes
IMPACT Pharmaceutics
IMPACT
Pharmaceutics
IMPACT Coatings
IMPACT
Coatings
IMPACT Micromachines
IMPACT
Micromachines
IMPACT Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT
Pharmaceuticals
IMPACT Atmosphere
IMPACT
Atmosphere
IMPACT Children
IMPACT
Children
IMPACT Religions
IMPACT
Religions
IMPACT Antioxidants
IMPACT
Antioxidants
IMPACT Life
IMPACT
Life
IMPACT Metals
IMPACT
Metals
IMPACT Biomolecules
IMPACT
Biomolecules
IMPACT Vaccines
IMPACT
Vaccines
IMPACT Education Sciences
IMPACT
Education Sciences
IMPACT Minerals
IMPACT
Minerals
IMPACT Horticulturae
IMPACT
Horticulturae
IMPACT Brain Sciences
IMPACT
Brain Sciences
IMPACT JPM
IMPACT
JPM
IMPACT Bioengineering
IMPACT
Bioengineering
IMPACT